Myth #1: The type of fat you are eating doesn’t matter
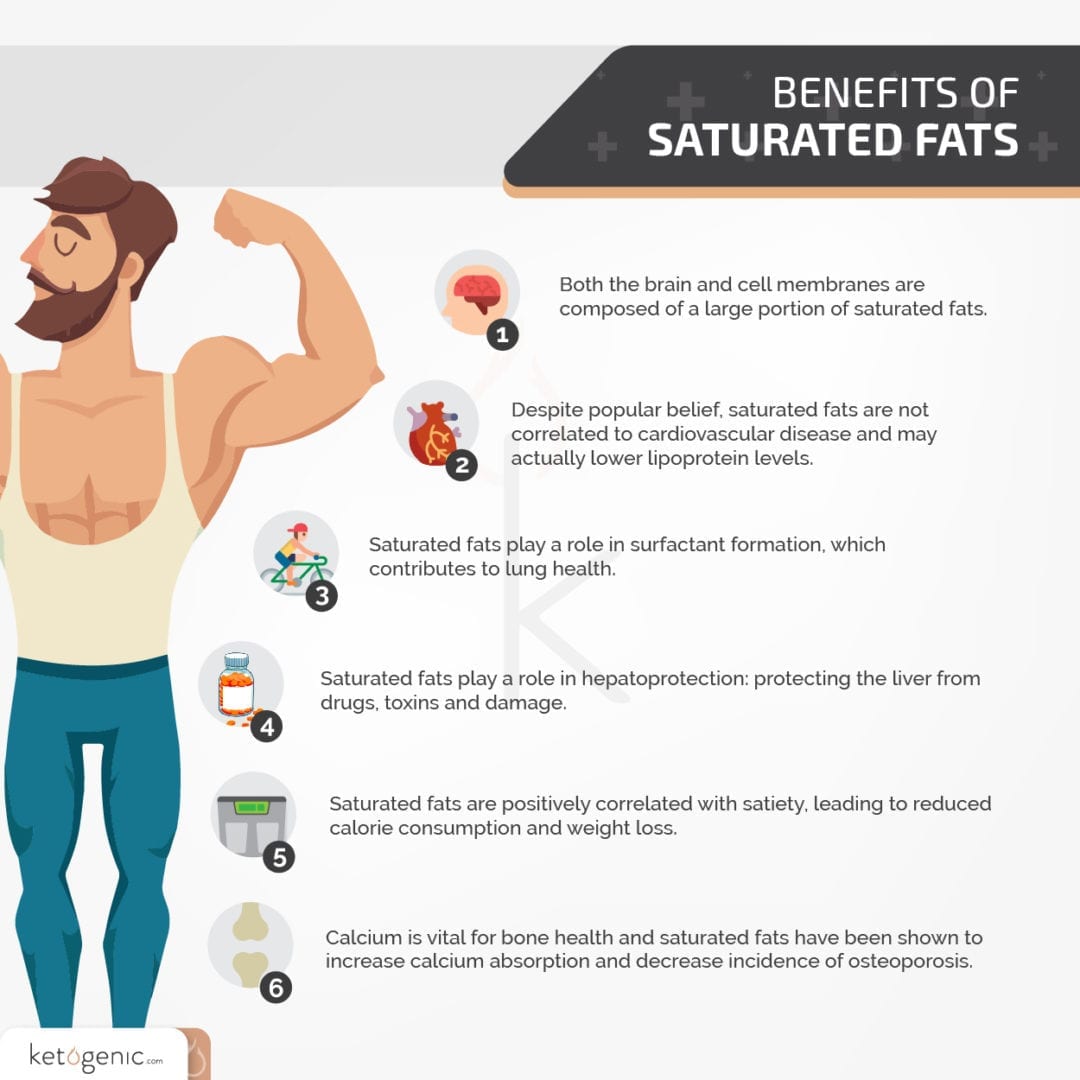
There are three types of fat: saturated, unsaturated, and trans. While trans fats should be avoided completely, there should be a balance between both saturated and unsaturated. [1]
Although there is a lot of controversy behind the actual ratio of unsaturated to saturated fats that should be consumed, saturated fat is not the demon the media portrays it to be.* In fact, recent research has debunked many of the cholesterol raising claims related to saturated fats and even found no correlation between heart disease and saturated fat consumption. [2] [3] Saturated fats found in foods such as butter, coconut oil, and animal fat provide many health benefits including but not limited to: cellular membrane functioning, hepatoprotection, hormone and immune system regulation. [4] [5]
“A meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies showed that there is no significant evidence for concluding that dietary saturated fat is associated with an increased risk of CHD or CVD.” – Tarino, 2010 [6]
Myth #2: If you do keto, you WILL get the keto-flu
 Headaches, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, irritability … none of these sound fun and all these are common symptoms of the “keto flu.”
Headaches, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, irritability … none of these sound fun and all these are common symptoms of the “keto flu.”
The term “keto flu” refers to a period of time, shortly after transitioning to keto, where your body is adapting to utilizing ketones over glucose. This adaptation process may produce terrible side effects; however, it is a common misbelief that you have to go through the keto flu. [7] Many people undergo the keto flu because they are not hydrating properly, regulating electrolyte consumption, or getting enough fat in their diet.
Here are some ways to avoid the keto flu:
- 1. Stay hydrated
- 2. Increase your sodium, potassium, and magnesium intake
- 3. Consume enough fat and consider MCT supplementation
Myth #3: You will lose your strength on a keto
Contrary to popular belief, research suggests that a well-formulated ketogenic diet will not reduce muscle mass or decrease strength gains. In a 2012 study a group of elite gymnasts were observed on a ketogenic diet and found so significant difference in strength after a month and showed a decrease in fat mass accompanied with a small increase in lean muscle mass. [8]
Myth #4: You will lose weight on keto, know how much you are eating
 While lowering your carbohydrate intake to a point of reaching nutrition ketosis does alter your body’s metabolism to burning a more efficient fuel source, it does not automatically guarantee you will lose body fat. While the ketogenic diet is a wonderful tool for weight loss, if you are still over-consuming an excess number of calories, it will be very difficult to lose body fat. However, research suggests individuals on a ketogenic diet do not over-consume as many calories as compared to traditional dieters (like low-fat diets) due to increased satiety from the increased fat in their diet. [9]
While lowering your carbohydrate intake to a point of reaching nutrition ketosis does alter your body’s metabolism to burning a more efficient fuel source, it does not automatically guarantee you will lose body fat. While the ketogenic diet is a wonderful tool for weight loss, if you are still over-consuming an excess number of calories, it will be very difficult to lose body fat. However, research suggests individuals on a ketogenic diet do not over-consume as many calories as compared to traditional dieters (like low-fat diets) due to increased satiety from the increased fat in their diet. [9]
While the butter-in-my-coffee craze is a great way to hit your fat macronutrient goals, keep in mind one stick of butter is around 800 calories. This is a 25-50% of most individuals recommended total daily caloric intake.
Myth 5: Raspberry ketones will help you get into ketosis
Despite the word “ketone” in the name, raspberry ketones have nothing to do with nutritional ketosis. There are three ketones produced in the human body: beta hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate, and acetone. BHB is the primary ketone produced in the body, while acetoacetate feeds into the pathway that form ketones, and very little acetone is produced. [10] When looking on the market for exogenous ketones, you will often find BHB salts or ester products because they are the most efficient of the three ketones. [11] A simple comparison of the organic structure (as show below) clearly shows the vast differentiation between the types of ketones. Raspberry ketones have no function within a ketogenic diet and simply will not induce ketogenesis or help you maintain a state of ketosis. [11] [12]
*As there will always be outliers to guidelines as such this, individuals with certain genetic disorders like as familial hypercholesterolemia or other cholesterol related genetic mutations may want to limit overall fat intake, especially saturated fats. Always consult your physician first if you are one of these individuals.
References
Iqbal M. P. (2014). Trans fatty acids – A risk factor for cardiovascular disease. Pakistan journal of medical sciences, 30(1), 194-7.
Hooper, L., Martin, N., Abdelhamid, A., & Davey, G. (2015, June 10). Reduction in saturated fat intake for cardiovascular disease. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26068959
De, R. J., Mente, A., Maroleanu, A., Cozma, A. I., Ha, V., Kishibe, T., . . . Anand, S. S. (2015, August 11). Intake of saturated and trans-unsaturated fatty acids and risk of all cause mortality, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26268692
Hwang, J., Chang, Y. H., Park, J. H., Kim, S. Y., Chung, H., Shim, E., & Hwang, H. J. (2011). Dietary saturated and monounsaturated fats protect against acute acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by altering fatty acid composition of liver microsomal membrane in rats. Lipids in health and disease, 10, 184. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-10-184
Carta, G., Murru, E., Banni, S., & Manca, C. (2017). Palmitic Acid: Physiological Role, Metabolism and Nutritional Implications. Frontiers in physiology, 8, 902. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00902
Siri-Tarino, P. W., Sun, Q., Hu, F. B., & Krauss, R. M. (2010, March). Meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies evaluating the association of saturated fat with cardiovascular disease. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20071648
Harvey, C., Schofield, G. M., & Williden, M. (2018). The use of nutritional supplements to induce ketosis and reduce symptoms associated with keto-induction: a narrative review.PeerJ, 6, e4488. doi:10.7717/peerj.4488
Paoli, A., Grimaldi, K., D’Agostino, D., Cenci, L., Moro, T., Bianco, A., & Palma, A. (2012, July 26). Ketogenic diet does not affect strength performance in elite artistic gymnasts. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22835211
Paoli, A., Bosco, G., Camporesi, E. M., & Mangar, D. (2015, February 02). Ketosis, ketogenic diet and food intake control: A complex relationship. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25698989
Dhillon, K. K. (2018, October 27). Biochemistry, Ketogenesis. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493179/
Stubbs, B. J., Cox, P. J., Evans, R. D., Santer, P., Miller, J. J., Faull, O. K., Magor-Elliott, S., Hiyama, S., Stirling, M., … Clarke, K. (2017). On the Metabolism of Exogenous Ketones in Humans. Frontiers in physiology, 8, 848. doi:10.3389/fphys.2017.00848
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; CID=21648, https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/21648 (accessed Dec 6, 2018)