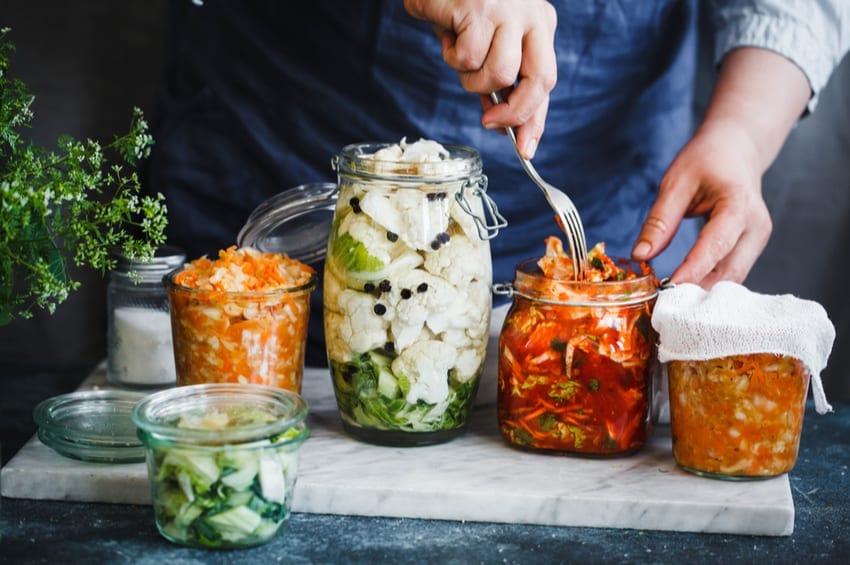
You might have heard about fermented foods through the grapevine. They might have seemed like some exotic or rural foods, but people from all over the globe frequently eat fermented foods due to the numerous health benefits. There’s plenty of buzz about fermented foods in the world of natural medicine and nutrition. So, what’s all the fuss about?
What are Fermented Foods?
Fermentation refers to an ancient method of food preservation. This process today is used to produce delicious nutrient-dense foods like kombucha tea and sauerkraut.
Fermented foods are rich in probiotics — a type of friendly bacteria that can benefit your health when you eat it. During the natural process of fermentation, microorganisms like yeast and bacteria convert carbs, such as sugar and starch, into acids or alcohol. The acids or alcohol are a natural preservative that gives fermented foods a tart and zesty flavor. Fermentation promotes the growth of these healthy probiotics.
Probiotic supplements are available, but they don’t deliver anywhere near as many healthy bacteria compared to fermented foods. Try switching out the fermented foods you eat for more bacterial diversity for your gut!
Fermented foods are safe for most people, but they might not necessarily be the right choice for everyone. Not all fermented foods are created equal and some products might have high levels of added sugar or other ingredients. If you’re trying fermentation at home, make sure you closely follow recipes. Unsterile equipment, incorrect temperatures, fermentation times, and other factors can make food unsafe to eat.
What are the Best Keto-Friendly Fermented Foods?
style=”font-style: normal; font-variant-ligatures: normal; font-variant-caps: normal; font-family: Roboto, sans-serif;”>Here are some of the best keto-friendly fermented foods:
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Certain cheeses
- Kombucha tea
- Kimchi
- Yogurt

You can ferment your choice of veggie, such as radish, and have fun with different types of fermented foods. Lots of fermented foods are keto-friendly! While most cheeses are fermented, this doesn’t mean they contain probiotics. The same applies to yogurt. Some healthy bacteria don’t survive certain manufacturing processes. Look for live and active cultures on food labels. Go for keto-friendly cheeses like Gouda where the good bacteria survive the aging process.
Pickles are another good source of probiotics. Pickles are cucumbers that have been pickled in a solution of water and salt. Pickles use their own naturally present lactic acid bacteria and are left to ferment for some time, giving pickles their sour taste. Remember that pickles that have been made with vinegar don’t contain live probiotics.
What are the Benefits of Fermented Foods?
Fermented foods are often more nutrient-dense than their unfermented form. The probiotics can boost immunity and restore the balance of friendly bacteria in your gut. Having more friendly gut bacteria and more diverse gut bacteria is beneficial for your digestive and general health.
Studies show fermented foods can help with digestion, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastrointestinal diseases [1] [2] [3] [4].
Research also shows fermented foods can relieve digestive symptoms like gas, bloating, and diarrhea [5] [6] [7].
The bacteria in your digestive system strongly impact your immune system and even your brain! Fermented foods can boost your immune system and reduce your risk of infections, such as the common cold [8] [9].
Eating probiotic-rich foods might also give you a speedier recovery when you’re sick. Many fermented foods are excellent sources of iron, vitamin C, and Zinc — all of which can strengthen your immune system. Fermentation also breaks down the nutrients in your food, making them easier to digest. For example, lactose is the natural sugar in milk that’s broken down into simple sugars during fermentation. This means that many people with lactose intolerance can still consume fermented dairy like yogurt and kefir [10] [11] [12] [13] [14].
Fermentation also assists with breaking down and destroying antinutrients, such as phytates, which are compounds found in nuts, seeds, legumes, and grains [15] [16].
In a nutshell, fermented foods can:
- Boost your immune system
- Aid digestion
- Reduce your risk of infection
- Accelerate your recovery when you’re sick
- Help break down and destroy antinutrients in foods
- Provide rich sources of vitamins and nutrients
Do You Eat Fermented Foods on Keto?
How do you incorporate fermented foods into your ketogenic diet? What are your favorite fermented food recipes?
References
Ritchie, M. L., & Romanuk, T. N. (2012). A meta-analysis of probiotic efficacy for gastrointestinal diseases. PLOS One, 7(4),
King, S., Glanville, J., Sanders, M. E., Fitzgerald, A., & Varley, D. (2014). Effectiveness of probiotics on the duration of illness in healthy children and adults who develop common acute respiratory infectious conditions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterology, 112(1), 41-54.
Hoveyda, N., Heneghan, C., Mahtani, K. R., Perera, R., Roberts, N., & Glasziou, P. (2009). A systematic review and meta-analysis: Probiotics in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterology,
Guyonnetm D., Chassany, O., Ducrotte, P., Picard, C., Mouret, M., Mercier, C-H, Matuchansky, C. (2007). Effect of a fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium Animalis DN-173 010 on the health-related quality of life and symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome in adults in primary care: A multicentre, randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 26(3), 475-486.
Dimidi, E., Christodoulides, S., Fragkos, K. C., Scott, S. M., & Whelan, K. (2014). The effect of probiotics on functional constipation in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 100(4), 1075-1084.
Eales, J., Gibson, P., Whorwell, P., Kellow, J., Yellowlees, A., Perry, R. H. J., Edwards, M., King, S., Wood, H., Glanville, J. (2017). Systematic review and meta-analysis: The effects of fermented milk with bifidobacterium lactis CNCM I-2494 and lactic acid bacteria on gastrointestinal discomfort in the general adult population.Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology, 10(1), 74-88.
Guarino, A., Lo Vecchio, A., & Canani, R. B. (2009). Probiotics as prevention and treatment for diarrhea. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 25(1), 18-23.
Ozen, M., Sandal, G. C., & Dinleyici, E. C. (2015). Probiotics for the prevention of pediatric upper respiratory tract infections: A systematic review. Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy, 15(1), 9-20.
Hao, Q., Lu, Z., Rong Dong, B., Huang, C. Q., & Wu, T. (2011). Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 7(9),
Guillemard, E., Tondu, F., Lacoin, F., & Schrezenmeir J. (2010). Consumption of a fermented dairy product containing the probiotic lactobacillus casei DN-114001 reduces the duration of respiratory infections in the elderly in a randomized controlled trial. British Journal of Nutrition, 103(1), 58-68.
Wintergerst, E. S., Maggini, S., & Hornig, D. H. (2007). Contribution of selected vitamins and trace elements to immune function. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism, 51(4), 301-323.
Maggini, S., Wintergerst, E. S., Beveridge, S., & Hornig, D. H. (2007). Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses.British Journal of Nutrition,
Chilton, S. N., Burton, J. P., & Reid, G. (2015). Inclusion of fermented foods in food guides around the world. Nutrients, 7(1), 390-404.
Hertzler, S. R., & Clancy, S. M. (2003). Kefir improves lactose digestion and tolerance in adults with lactose maldigestion. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 103(5), 582-587.
Hotz, C., & Gibson, R. S. (2007). Traditional food-processing and preparation practices to enhance the bioavailability of micronutrients in plant-based diets.The Journal of Nutrition, 137(4), 1097-1100.
Center for Applied Nutrition. (2019). Eat Better, Feel Better,