Urine is composed of primarily water and certain excreted minerals. The major components of human urine include water, urea, chlorine, sodium, potassium, and creatinine. Urine may also include other ions, as well as both organic and inorganic compounds. [1] The presence of cells and molecules like blood, glucose, and protein may be indicative of a pathological condition. But, what about ketones in urine? Is it normal? Or is it a sign of a bigger issue?
What If You’re Not Following a Keto Diet?
On a standard, high-carb diet, the human body runs on glucose (from carbs) for energy. On a ketogenic diet, carbs are limited and thus the body must burn fat as a fuel source. Fatty acids are broken down into ketones. Excess ketones (more specifically acetoacetate) are excreted in the urine. [2]
Detecting ketones in urine while following a low-carb diet or practicing intermittent fasting is completely normal and not indicative of a pathological condition. In fact, it is one of the simplest and non-invasive ways to test at home. [3]

Ketones in Urine If You Aren’t Following the Ketogenic Diet
Small amounts of ketones in the urine are normal even if you aren’t following a ketogenic diet. As previously mentioned, fasting increases ketone bodies, which can be excreted in the urine. Every time you go to sleep, you are not eating, and thus fasting for around 8+ hours. If you don’t eat immediately after waking up or right before going to bed, you are inadvertently practicing intermittent fasting, which can elevate ketone levels. [3]
However, if ketone levels are high in individuals who are not following a low-carbohydrate diet or practicing fasting may be indicative of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). DKA is different from ketosis and is in no way related to the ketogenic diet. It is a complication of diabetes, more often type 1 diabetes. [4]

Since the body thinks that it is starving, fatty acids are rapidly broken down into ketone bodies. The amount of ketones products is far greater than anything a ketogenic diet would produce (think 0.5-1mmol vs 10-15mmol of ketones). [6]
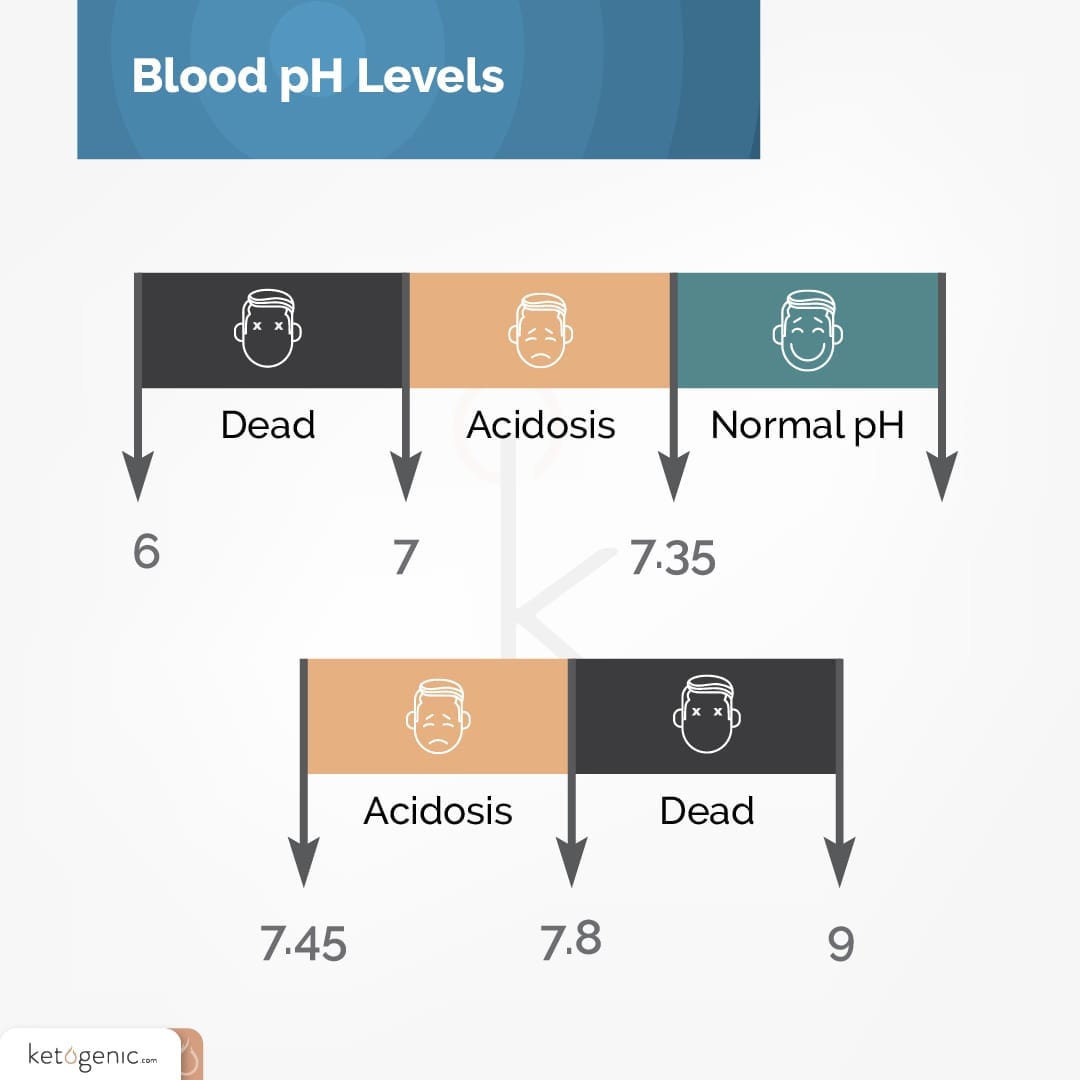
Since ketones are a naturally acidic compound, a great and rapid increase in the presence of ketones triggers a drop in blood pH. This is a life-threatening medical condition that can lead to permanent organ damage and even death if left untreated.
Talk to your doctor or other health care professional immediately if high levels of ketones are present in your urine and you are not following a ketogenic diet.
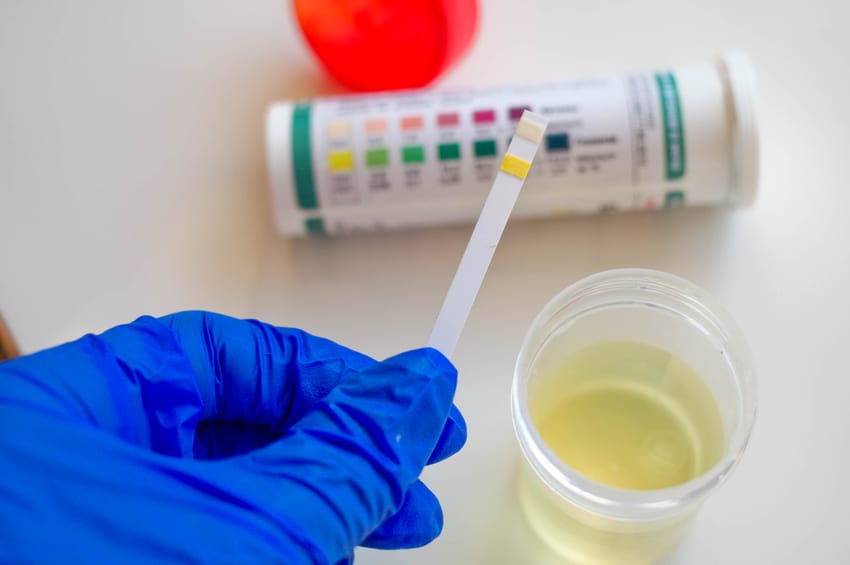
How to Test Ketones In Urine
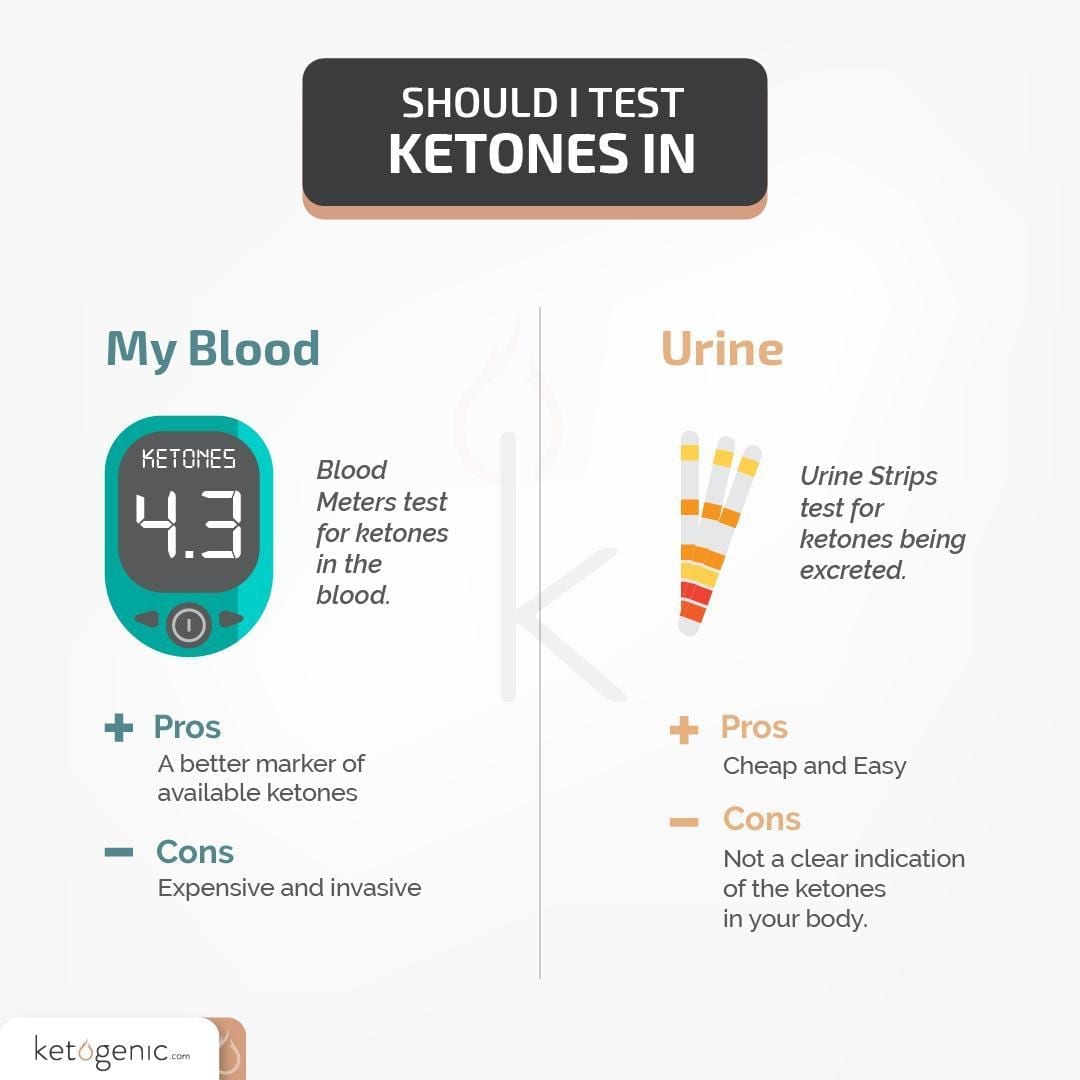
Testing urine ketone levels is one of the simplest ways to determine whether or not you are in ketosis. That being said, it is also considered less accurate and reliable than other methods (like testing blood ketone levels).
Urine test strips are available over-the-counter in many drug stores and even some mass retailers like Walmart. Simply urinate on the indicated portion of the testing strip, allow to sit for as long as the packaging directs (typically 1-3 minutes), and match the color indicating strip with the reference on the box or packaging.
Both blood and urine ketone tests are available over-the-counter; however, blood tests tend to be the most accurate. Blood sugar levels can only be tested through blood.
For more information on how to test blood glucose levels and check for ketones in your blood, try reading our article: How to Measure Blood Glucose and Ketone Levels.
References
MOZOLOWSKI W. Chemical composition of normal urine. Lancet. 1948 Mar 13;1(6498):423. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(48)90292-x. PMID: 18904296.
Masood W, Annamaraju P, Uppaluri KR. Ketogenic Diet. [Updated 2021 Jun 11]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/
Park, S., Zhang, T., Wu, X., & Yi Qiu, J. (2020). Ketone production by ketogenic diet and by intermittent fasting has different effects on the gut microbiota and disease progression in an Alzheimer's disease rat model. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition, 67(2), 188–198. https://doi.org/10.3164/jcbn.19-87
Dhatariya KK, Glaser NS, Codner E, Umpierrez GE. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 May 14;6(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-0165-1. PMID: 32409703.
Gosmanov AR, Kitabchi AE. Diabetic Ketoacidosis. [Updated 2018 Apr 28]. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, et al., editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279146/
Cartwright, M. M., Hajja, W., Al-Khatib, S., Hazeghazam, M., Sreedhar, D., Li, R. N., … & Carlson, R. W. (2012). Toxigenic and metabolic causes of ketosis and ketoacidotic syndromes. Critical care clinics, 28(4), 601-631.