The ketogenic diet stands out from other diets because it induces a unique metabolic state, rather than just reducing calories. Other diets work by limiting calorie intake and causing you to be in a caloric deficit. While the ketogenic diet does work to reduce calorie intake, it is also beneficial by putting you in a metabolic state of ketosis.
What Is Ketosis?

Webster’s Dictionary defines ketosis as “an abnormal increase of ketone bodies in the body”. [1]
The human body typically runs on glucose (from carbohydrates) for energy, but when carbohydrates are restricted, the body can’t break down carbs to create glucose. Instead, it will break down fatty acids to create ketone bodies, in a process known as ketogenesis. Since this is not considered the norm for most of the world (since most people consume a high amount of carbohydrates), it is defined as an abnormal state. [2] [3]
How Do You Get Into Ketosis?
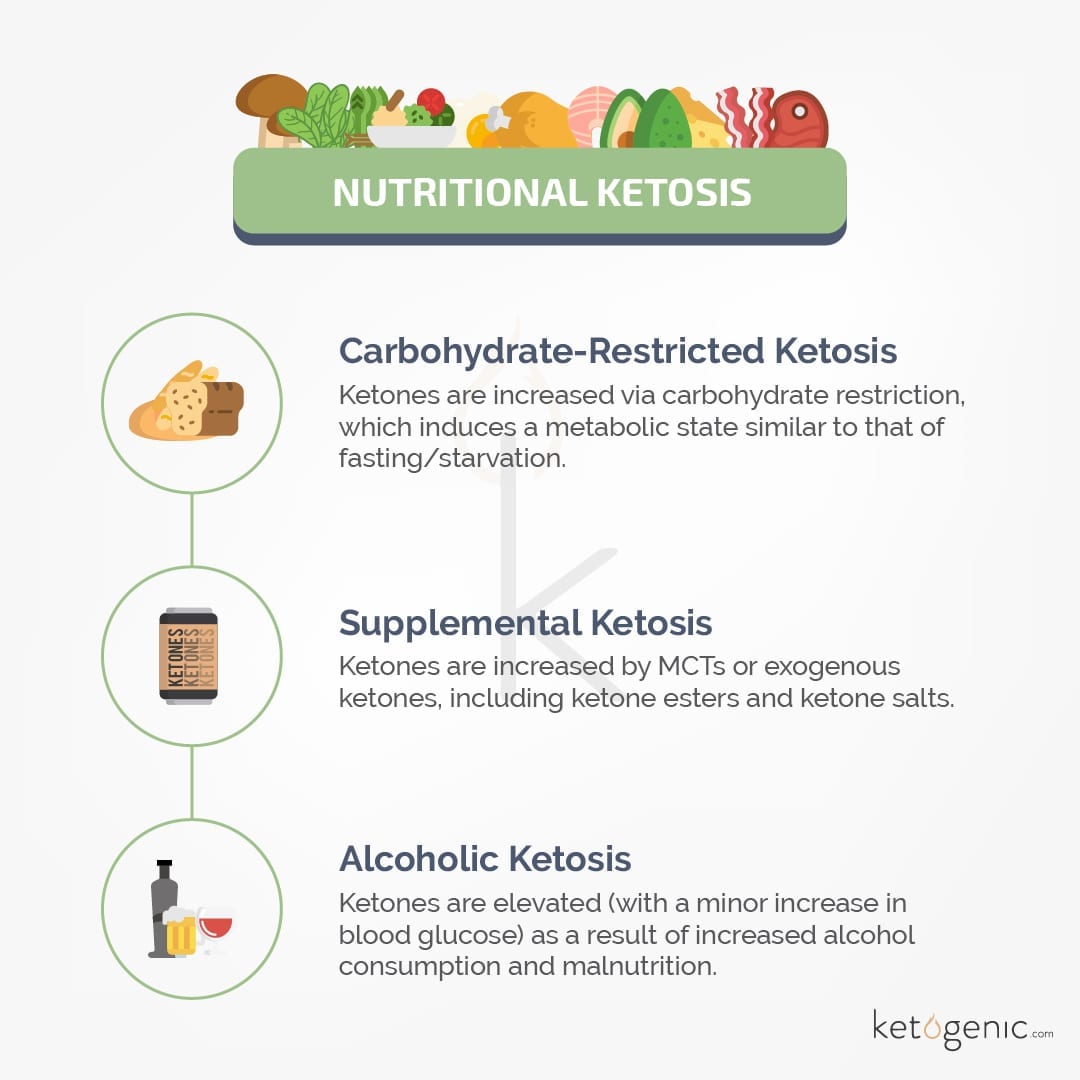
You can achieve the metabolic state of ketosis in several ways, some of these methods are beneficial and others are harmful. Fasting and nutritional ketosis describe increased ketone production through fasting (not consuming food for an extended period of time) and consuming a diet low in carbohydrates (i.e. a ketogenic diet) respectively.
Alcohol-induced ketogenesis and diabetic ketoacidosis are two different causes of ketone production that are harmful and are not the same as reducing carbohydrates or fasting to trigger ketone production. For more information on those, check out our article: Are There Different Types of Ketosis?
How Long Does It Take To Get Into Ketosis?
While it differs from person to person, most individuals are able to achieve the metabolic state of ketosis in 2-3 days; however, it may take up to a week for some individuals. Intermittent fasting, supplementing with exogenous ketones, supplementing with MCT oil/coconut oil, and high-intensity exercise can all help you increase ketone production and get into this metabolic state faster.
Do You Have Any Tips To Increase Ketone Production?
Share your best advice and tips with the community!
References
“Ketosis.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/ketosis. Accessed 10 Mar. 2021.
Masood W, Annamaraju P, Uppaluri KR. Ketogenic Diet. [Updated 2020 Dec 14]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499830/
Dhillon KK, Gupta S. Biochemistry, Ketogenesis. [Updated 2021 Feb 17]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK493179/