Simply put, hyperglycemia means high blood sugar. The pre-fix hyper means high or above normal and glycemia refers to blood glucose. Diabetes is directly correlated with hyperglycemia because it is a disease of high blood glucose levels. Diabetes mellitus affects roughly 387 million people around the world, so the question of how you can lower your blood sugar levels is an important one. [1] [2]
What Is Considered High Blood Glucose?
Hyperglycemia is defined as having a fasted/resting blood glucose level greater than 125 mg/dL and a glucose level >180 mg/dL 2 hours after eating. [1]
Impaired glucose tolerance, or pre-diabetes, is measured having a fasting glucose level between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL. Levels between 140-180 mg/dL 2 hours after eating are considered elevated and pre-diabetic. [1]
Diabetes is diagnosed when individuals fasting blood glucose levels are above 125mg/dL. [1]

What Causes Hyperglycemia?
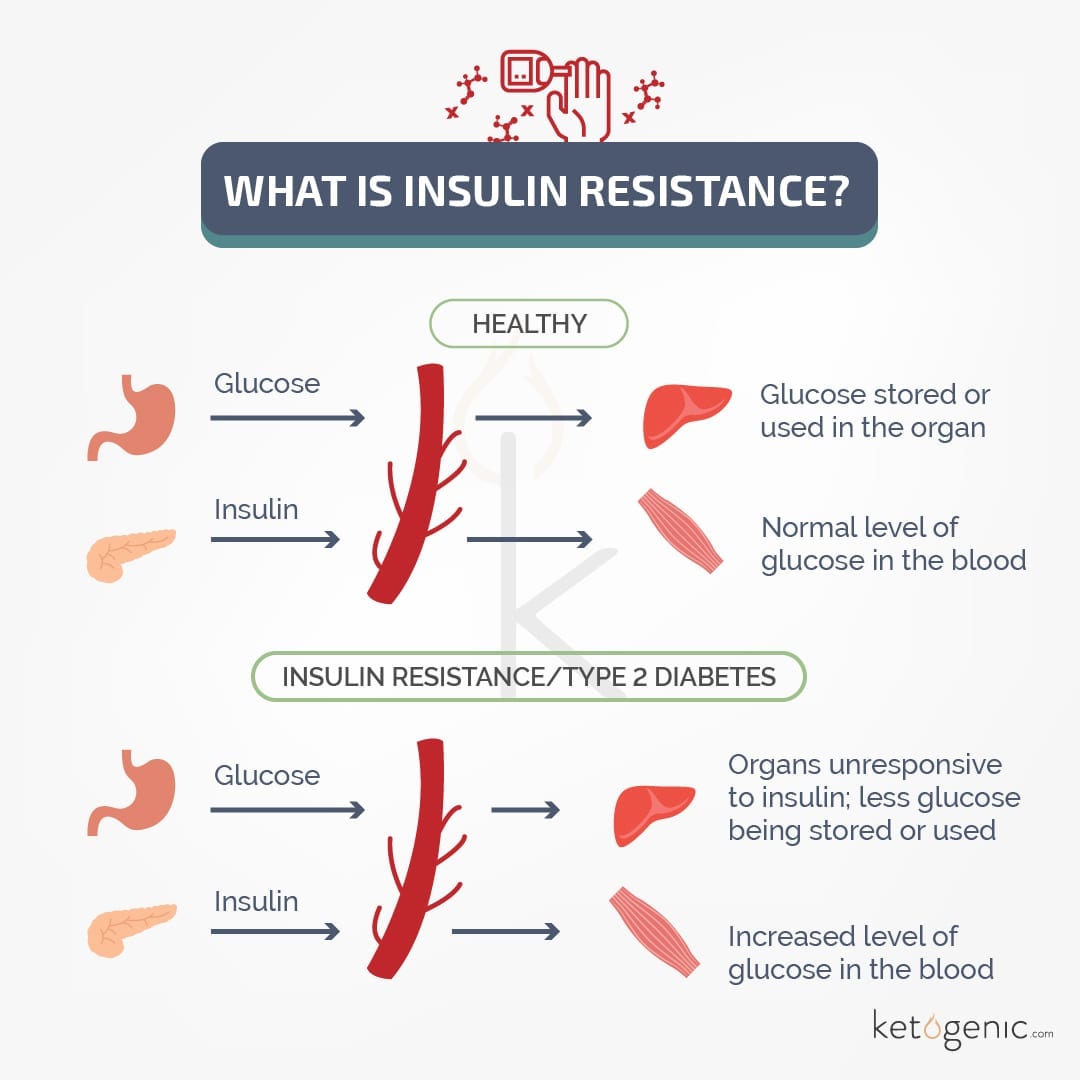
Insulin is the most important regulator of blood glucose levels. In order to maintain homeostasis, insulin must be functioning properly.
When food is consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose (the simplest sugar). Insulin is released by beta-islet cells in the pancreas. Insulin binds to insulin receptors and signals cells to allow glucose into the cell (uptake/ utilization). If this process is impaired at any step, there will be a shift in glucose balance.

- Impaired insulin secretion
- Impaired glucose utilization/uptake into cells
- Increased glucose production
Secondary causes of hyperglycemia include the following: [1]
- Gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) [4]
- Insulin resistance caused by endocrine disorders (such as Cushing’s Disease or pheochromocytoma
- Use of glucocorticoids (i.e. hydrocortisone, prednisolone, cortisone)
- Pancreatic insufficiency or disease
What are the Risk Factors of Hyperglycemia?
Risk factors for having blood glucose levels generally revolve around insulin resistance. The following are some of the major risk factors for hyperglycemia:
- High body fat percentage [1]
- Family history of Type 2 Diabetes [1]
- Diseases that cause impaired insulin sensitivity (such as PCOS) [1]
Additionally, individuals of Hispanic, Asian, Pacific Islander, Native American, and African American descent are more likely to develop high blood sugar. [1]
What are the Symptoms of High Blood Sugar?
Symptoms of hyperglycemia include:
- Polyuria (increased urination)
- Polydipsia (increased thirst)
- Weight loss
When left untreated hyperglycemia can lead to serve neurological issues and cause nerve damage. Long-term complications can be life-threatening and include retinopathy (damage to the retina) and neuropathy (damage to nerves). [5] [6]
How is Hyperglycemia Treated?
High blood glucose is treated with dietary and lifestyle interventions and/or insulin (when necessary). Type 2 diabetes may also be treated with diabetes medication, like metformin, which works to lower blood glucose levels. [1]
Can the Ketogenic Diet Lower Blood Glucose Levels?
The simplest way to lower blood glucose levels is to reduce the consumption of foods high in glucose. This is the reasoning behind utilizing a ketogenic diet in the treatment of hyperglycemia.
The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, moderate-protein, and high-fat diet. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
Reducing carbohydrate consumption will reduce the need for insulin secretion, helping to improve insulin resistance (restoring receptor sensitivity) and help normalize resting blood glucose levels. [7]
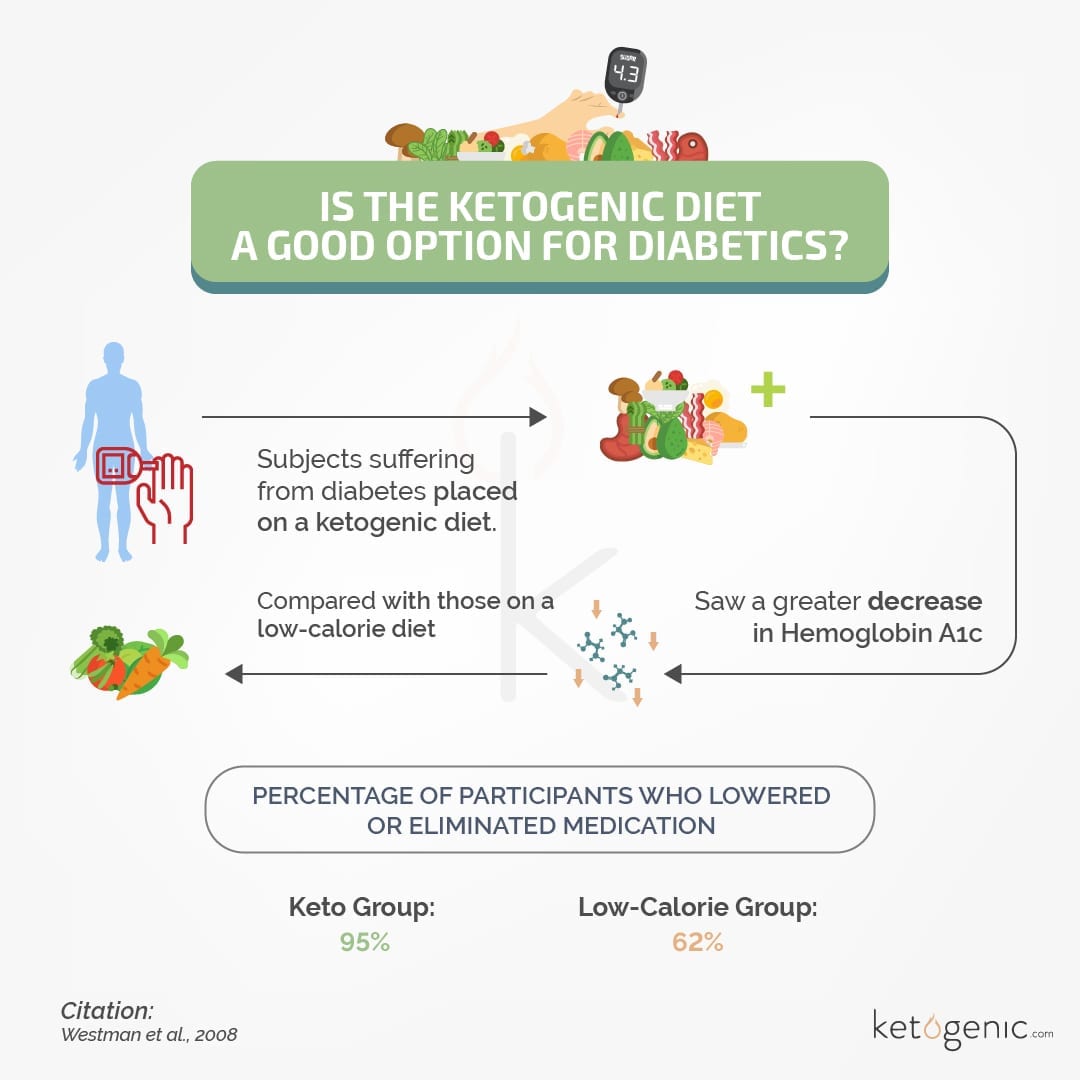
One meta-analysis found that a ketogenic diet decreased fasting blood glucose levels by an average of 1.29 mmol/ L or 5.17 mg/dL. Average HbA1c (glycosylated hemoglobin) was decreased by 1.07. [8]
Another study of 28 individuals found that after 16 weeks following a ketogenic diet, HbA1c levels decreased by 16%. [9]
Do You Use a Ketogenic Diet To Lower Blood Sugar Levels?
Comment below and share your experience with the community!
References
Mouri MI, Badireddy M. Hyperglycemia. [Updated 2021 May 10]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK430900/
El Khoury G, Mansour H, Kabbara WK, Chamoun N, Atallah N, Salameh P. Prevalence, Correlates and Management of Hyperglycemia in Diabetic Non-critically Ill Patients at a Tertiary Care Center in Lebanon. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2019;15(2):133-140. doi: 10.2174/1573399814666180119142254. PMID: 29357807.
Smith WD, Winterstein AG, Johns T, Rosenberg E, Sauer BC. Causes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in adult inpatients. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2005 Apr 1;62(7):714-9. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/62.7.714. PMID: 15790798.
Bashir M, Naem E, Taha F, Konje JC, Abou-Samra AB. Outcomes of type 1 diabetes mellitus in pregnancy; effect of excessive gestational weight gain and hyperglycaemia on fetal growth. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2019 Jan - Feb;13(1):84-88
Jensen T, Deckert T. Diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy and neuropathy. Generalized vascular damage in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Horm Metab Res Suppl. 1992;26:68-70. PMID: 1490695.
Muc, R., Saracen, A., & Grabska-Liberek, I. (2018). Associations of Diabetic Retinopathy with Retinal Neurodegeneration on the Background of Diabetes Mellitus. Overview of Recent Medical Studies with an Assessment of the Impact on Healthcare systems. Open medicine (Warsaw, Poland), 13, 130–136. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2018-0008
Westman EC, Tondt J, Maguire E, Yancy WS Jr. Implementing a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Sep;13(5):263-272. doi: 10.1080/17446651.2018.1523713. PMID: 30289048.
Yuan, X., Wang, J., Yang, S., Gao, M., Cao, L., Li, X., Hong, D., Tian, S., & Sun, C. (2020). Effect of the ketogenic diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and lipid metabolism in patients with T2DM: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrition & diabetes, 10(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41387-020-00142-z
Yancy, W. S., Jr, Foy, M., Chalecki, A. M., Vernon, M. C., & Westman, E. C. (2005). A low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet to treat type 2 diabetes. Nutrition & metabolism, 2, 34. https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-7075-2-34