Are Raspberry Ketones a Scam? Do They Help You Get Into Ketosis?

Just because the word ketone is in the name, doesn’t mean it has anything to do with ketosis or the ketogenic diet. In fact, ketone is actually just the name of an organic structure. Raspberry ketones have been marketed as a fat-burning keto supplement that will help you lose weight, but the scientific evidence has something else to say.
What Are Ketones?
The term ketone describes organic molecules that have a carbonyl group bonded to two hydrocarbons (R2C=O). Ketones are made through the oxidation of a secondary alcohol. [1]
Ketogenesis describes the process of generating ketone bodies.
2 acetyl-CoA are converted into acetoacetyl-Coa via the enzyme thiolase.
HMG-CoA synthase enzyme catalyzes its conversion into B-hydroxy-B-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA).
HMG-CoA Lyase then catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA into acetoacetate. Acetoacetate can then be converted into acetone or beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB). [2]

What Ketones Are Produced In Ketosis?
Besides while breastfeeding (babies are keto), humans utilize glucose as a primary energy source. Glucose is primarily obtained through the consumption and breakdown of carbohydrates ( aka glycolysis). Glucose can also be obtained from non-carbohydrate sources in a process known as gluconeogenesis. Additionally, glucose can also be created through the breakdown of glycogen in a process known as glycogenolysis.
In times of carbohydrate restriction, glucose is sparse, and thus so is energy. The human body converts fatty acids into ketones as an energy source. When in a metabolic state of ketosis three ketone bodies are generated: acetone, acetoacetate, and BHB. Acetone is a volatile ketone and is released in the breath. Acetoacetate is excreted in the urine and BHB can be found in the blood. [3]
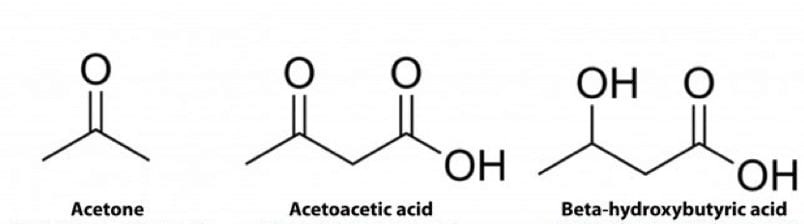
These three molecules are endogenous ketones, meaning they are produced within the human body. Exogenous ketones refer to ketones that are made outside of the body. Exogenous ketones are common supplements consumed on the ketogenic diet to increase blood ketone levels.
What Are Raspberry Ketones?
Raspberry ketones are aromatic compounds found commonly in raspberries. “Aromatic” is a term that describes an organic molecule with one or more rings. Ketone just describes the organic structure and raspberry is derived from its primary source. [4]

Will Raspberry Ketones Help You Get Into Ketosis? Are They Exogenous Ketones?
No, raspberry ketones will not help you get into ketosis. They are not an exogenous ketone and have absolutely no effect on blood ketone levels. Despite the term ketone in the name, they actually have nothing to do with the ketogenic diet or being in a metabolic state of ketosis.
Are Raspberry Ketones a Scam?
Many raspberry ketone supplements claim to help the body burn fat, reduce appetite, and produce weight loss in humans. The published research, however, does not support this claim. No clinical trials support this supplement as an effective weight loss strategy in humans.
There is limited research on the effects of raspberry ketone consumption in humans at all. One animal study found that supplementation may help reduce appetite but had no effect on adiposity (having excess fat) whatsoever. [5] Another found that consuming raspberry ketones may have negative side effects and could actually be harmful. [4]
While this was an animal study (meaning it doesn’t directly translate to humans), it can be used as cautionary evidence towards taking weight loss supplements. This study found that supplementation led to elevated ALT (a liver enzyme) levels, as well as blood glucose levels. [4]
Final Thoughts
Raspberry ketone pills are not a miracle weight loss drug. These supplements won’t help you get into ketosis and they aren’t going to magically melt all the fat off your body. Research does not support these pills as an effective weight loss solution in humans. Save your money and don’t be scammed by these pills!
References
Nomenclature of Aldehydes & Ketones. (2020, December 16). Retrieved August 12, 2021, https://chem.libretexts.org/@go/page/746
Dhillon KK, Gupta S. Biochemistry, Ketogenesis. 2021 Feb 17. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 Jan–. PMID: 29630231.
Laffel L. (1999). Ketone bodies: a review of physiology, pathophysiology and application of monitoring to diabetes. Diabetes/metabolism research and reviews, 15(6), 412–426. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1520-7560(199911/12)15:6<412::aid-dmrr72>3.0.co;2-8
Mir TM, Ma G, Ali Z, Khan IA, Ashfaq MK. Effect of Raspberry Ketone on Normal, Obese and Health-Compromised Obese Mice: A Preliminary Study. J Diet Suppl. 2021;18(1):1-16. doi: 10.1080/19390211.2019.1674996. Epub 2019 Oct 11. PMID: 31603036.
Cotten BM, Diamond SA, Banh T, Hsiao YH, Cole RM, Li J, Simons CT, Bruno RS, Belury MA, Vodovotz Y. Raspberry ketone fails to reduce adiposity beyond decreasing food intake in C57BL/6 mice fed a high-fat diet. Food Funct. 2017 Apr 19;8(4):1512-1518. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01831a. PMID: 28378858.









