Word’s out that the ketogenic diet and lifestyle promotes weight loss. Obesity is surging and associated with numerous health problems, such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke [1]. People are turning to keto to budge the bulge and improve health, wellness, and quality of life.
With keto, weight loss can occur quickly and most weight loss in the first couple of weeks is typically from water. This loss of water-weight is due to the carbohydrate restriction since carbohydrates retain water when stored in the body. The body also reduces glycogen stores (or stored glucose) in the muscles [2] At this point, weight loss can slow and continue at a steadier rate.
Total weight loss depends on the starting weight. With a higher starting weight, weight loss typically occurs more rapidly.
As always, it’s important to stay hydrated, get regular appropriate exercise, plenty of rest, and consume nutritious foods to achieve healthy weight loss on keto. Continuing the keto lifestyle can help maintain weight loss results and a healthy body weight.

What Does the Research Show About Keto for Weight Loss?
The increase in fat consumption and reduction in sugar intake is the main concepts of the ketogenic diet. All calories aren’t equal. The calories in a sugary candy bar don’t deliver the same nutritious value to the body as the same amount of calories in broccoli. Different macronutrients and types of calories have different effects on the body, fat storage, and metabolism.
Studies repeatedly show that a lower carbohydrate ketogenic diet is superior for long-term weight loss when compared to a low-fat diet. Essential fatty acids really are essential to thrive and survive and they can also assist with weight loss [3]
From clinical studies to personal stories, the evidence is clear that the ketogenic diet is effective for weight loss [4] [5]Insulin also plays a role. Insulin is a hormone that’s released by the pancreas with sugar consumption. This shifts the metabolism into a fat-storage mode. The insulin hormone stores sugar or glucose into our cells where it’s used for energy. Sugar can’t properly get into most of the body’s cells without insulin [6] [7]
Lowering sugar intake on the ketogenic diet lowers the need for insulin and helps shift the body into a fat-burning mode instead of a fat-storage mode. Research points to the weight loss benefits of ditching sugar and sugar-sweetened beverages — a necessity when going keto [8].
Certain other factors might also be involved with weight loss, such as hormones, toxicity, and stress.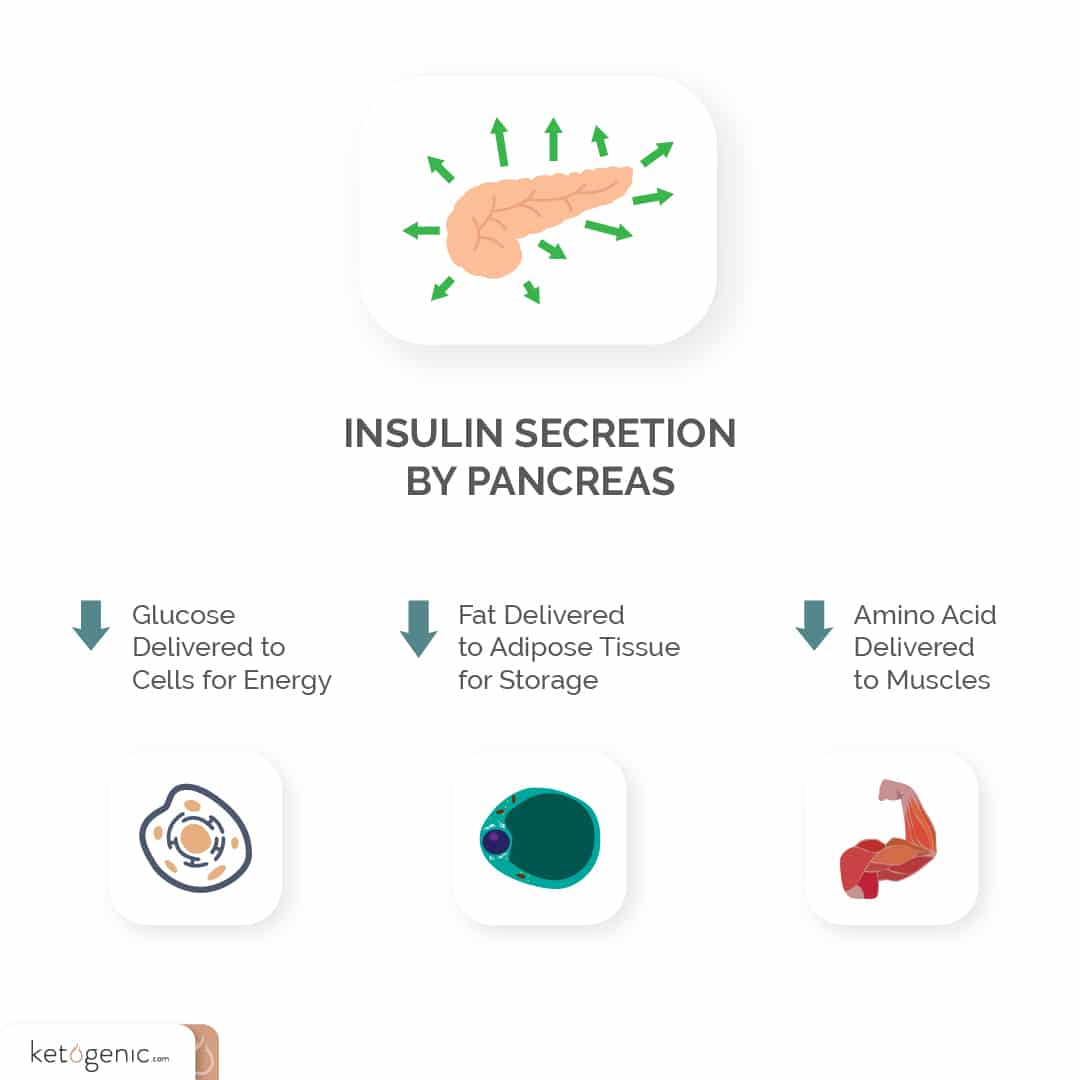
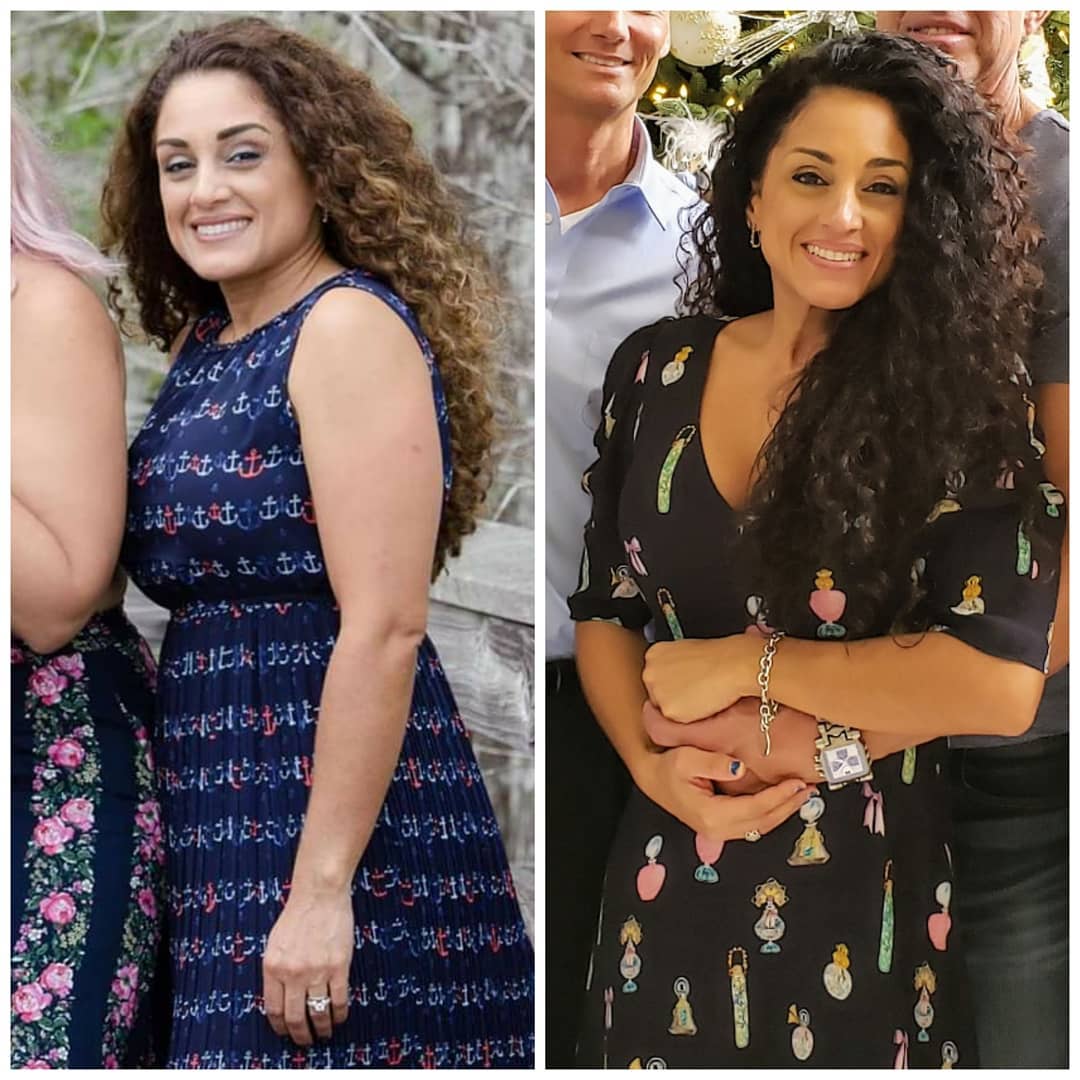
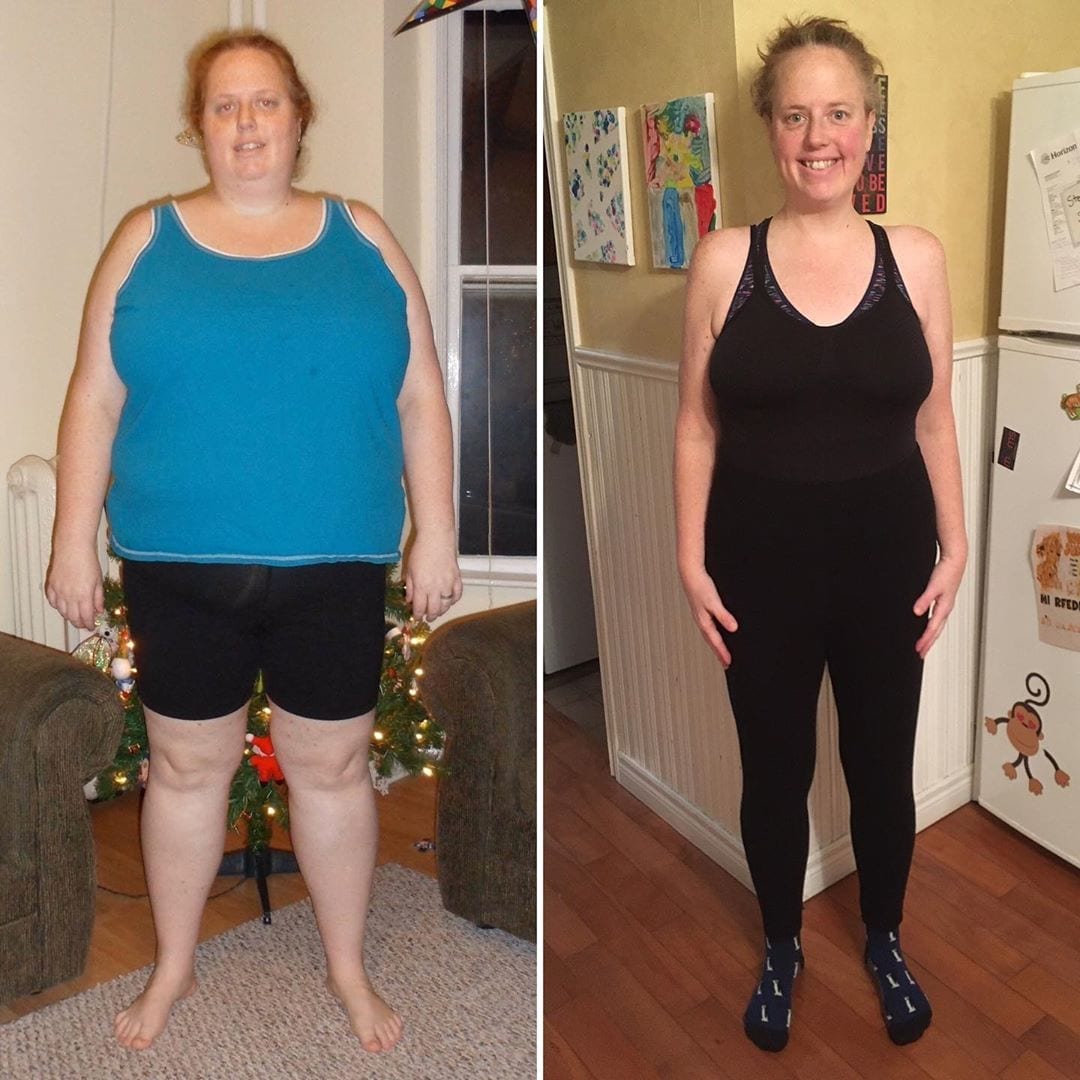
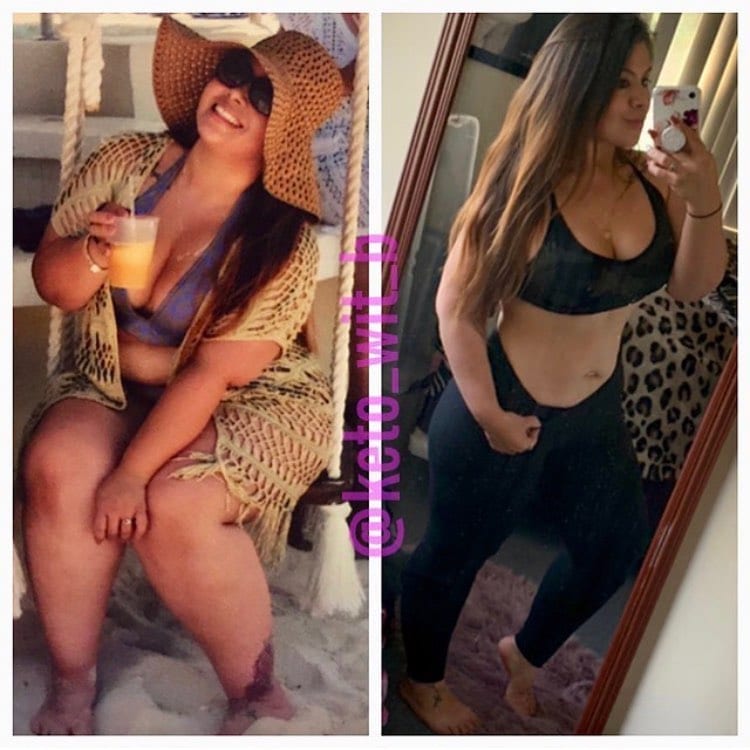
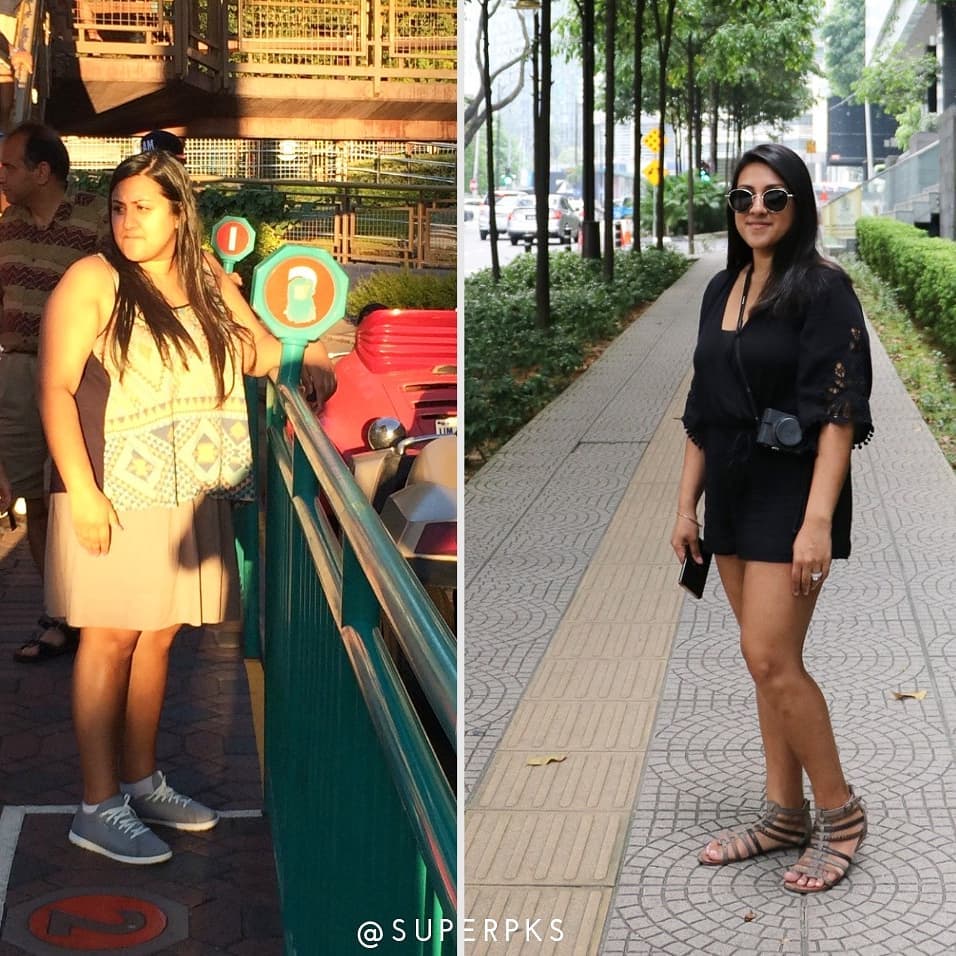
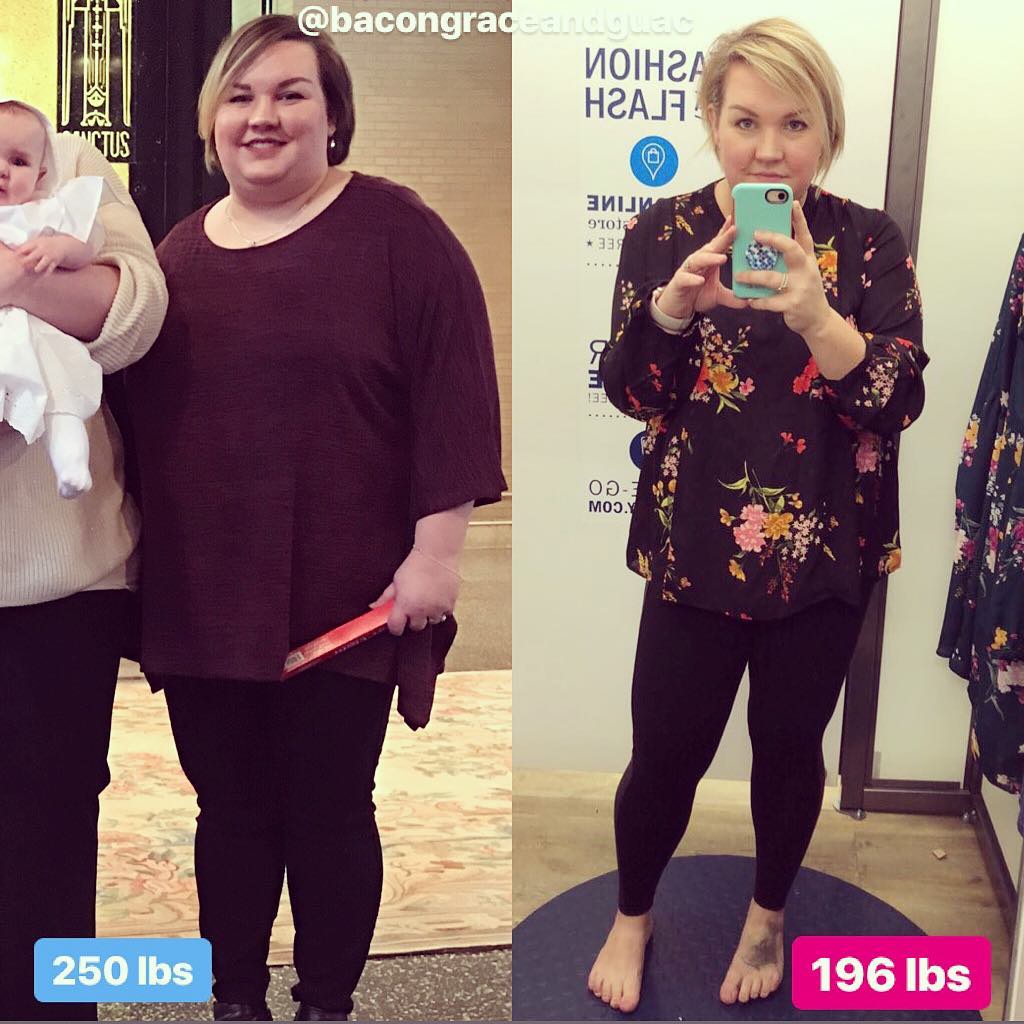
Check Out Some of Our Keto Weight Loss Success Stories!
Get inspired by our keto weight loss success stories and see how people like Crystal and Jessica are shedding the pounds with a healthy keto lifestyle.
Have your friends, family, and like-minded keto community members support your weight loss journey. Studies show even teens can get on board and stay on board the keto train to reap the many health benefits, including weight loss [9]
Why not join our keto club where you receive exclusive articles and Ebooks, doctor guides, and so much more?
Recipes for Weight Loss on Keto
Check out our countless recipes for delicious dishes and tasty treats that promote weight loss, satiety, and most importantly…health. When craving old favorites and delectable delicacies, the ketogenic recipe section is the place to peruse. Here are a few to get started with:
- Keto pie crust
- Keto cauliflower pizza
- Keto corn bread
- Keto chocolate ice cream
- Keto blueberry muffins
- Keto chili
Are You Planning on Losing Weight with Keto? Do You have a Keto Weight Loss Success Story to Share?
Comment below and let’s talk keto and weight loss!
References
Kreitzman, S. N., Coxon, A. Y., & Szaz, K. F. (1992). Glycogen storage: illusions of easy weight loss, excessive weight regain, and distortions in estimates of body composition.American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 56(1),
Bueno, N. B., Vieira de Melo, I. G., De Oliveira, S. L., & Da Rocha Ataide, T. (2013). Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. British Journal of Nutrition, 110(7), 1178-1187.
Westman, E. C., Mavropoulos, J., Yancy Jr, W. S., & Volek, J. S. (2003). A review of low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets.Current Atherosclerosis Reports, 476-483.
Dashti, H. M., Al-Zaid, N. S., Mathew, T. C., Al-Mousawi, M., Talib. H., Asfar, S. K., & Behbahani, A. I. (2006). Long term effects of ketogenic diet in obese subjects with high cholesterol level. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 286
Mayo Clinic. Insulin (parenteral route).
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Insulin resistance & prediabetes.
Chen, L., Appel, L. J., Loria, C., Lin, P., Champagne, C. M., Elmer, P. J., Ard, J. D., Mitchell, D., Batch, B. C., Svetkey, L. P., & Caballero, B. (2009). Reduction in consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is associated with weight loss: the PREMIER trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(5), 1299-1306.
Mady, M. A., Kossoff, E. H., McGregor, A. L., Wheless, J. W., Pyzik, P. L., & Freeman, J. M. (2003).The ketogenic diet: adolescents can do it, too. Epilepsia,