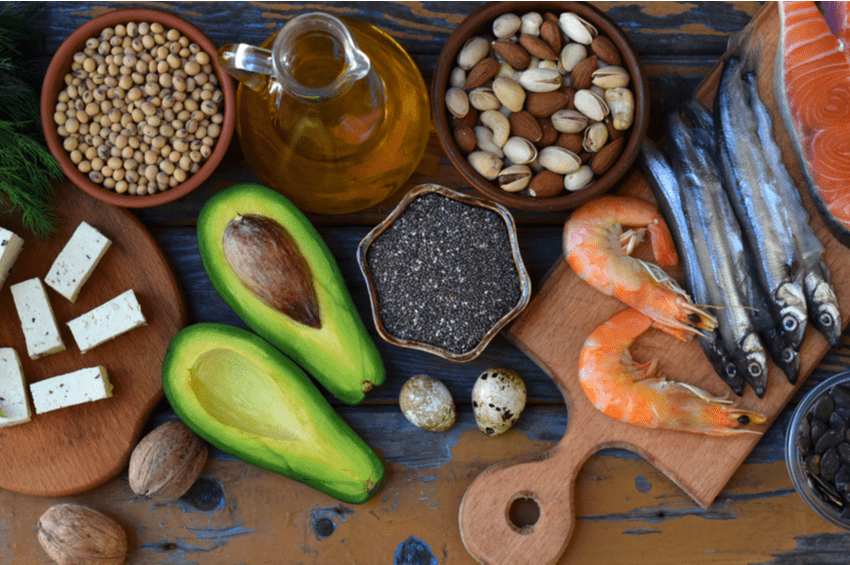
Which foods are rich in those health-boosting dietary omega-3 fatty acids? Where can you find keto-friendly food sources of omega-3 fatty acids and tasty recipes? Look no further than Ketogenic.com!
Most mainstream health organizations recommend healthy adults get at least 250-500mg of omega-3s per day. [1] [2]
Check out our detailed article for more info on the different types of omega-3s. The three main types are EPA, DHA, and ALA. EPA and DHA are primarily present in animal foods, and ALA is primarily present in plant foods. Omega-3s have been shown to lower the risk of heart disease, dementia, depression, and more. [3] [4]
For the benefit of your body and brain, let’s discuss the top sources of omega-3s and the tastiest ways to incorporate them into your keto diet.
Top Omega-3 Food Sources!
High concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids are found in fatty fish like mackerel, algae, and some high-fat plant foods. Here are some of the top sources:
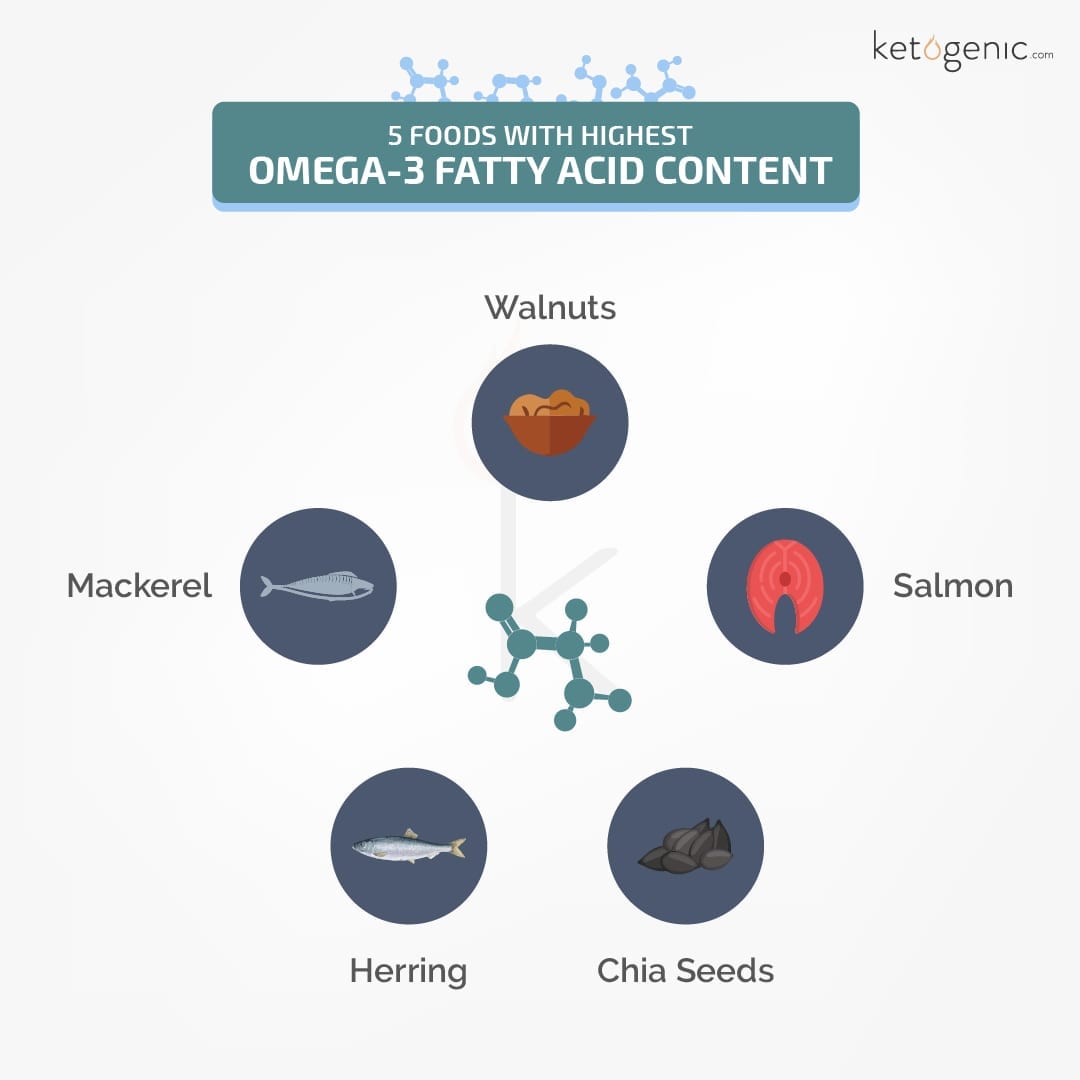
1.) Salmon
Salmon is just as nutritious as it is vibrant in color. When you bite into a mouthwatering piece of salmon, you’ll be getting high-quality protein and various nutrients, including selenium, vitamin D, and B vitamins. [5]
For example, 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of cooked, farmed Atlantic salmon has 2,260 mg of omega-3s.
Most health advocates believe the best quality and healthiest fish is wild-caught instead of farmed. Interesting note: wild-caught salmon is significantly darker and more of a reddish-pink in color compared to farmed salmon, which is more of a lighter pink. You can typically tell if salmon is farmed or wild-caught just by looking at the color!
Boost your omega-3s with this baked salmon keto recipe or this smoked salmon appetizer.



2.) Mackerel
Mackerel are small, flavorful, nutrient-dense, fatty fish that is usually smoked and consumed as whole fillets!
Just one 3.5-ounce (100 gram) serving provides 100% of your RDI (reference daily intake) for selenium and 200% for vitamin B12.
3.5 ounces (100 grams) of mackerel also gives you 5,134 mg of omega-3s. [6]
3.) Oysters
Oysters are nutritious and eaten as a snack, appetizer, or whole meal worldwide. Oysters aren’t just a fancy aphrodisiac; they also provide plenty of zinc, copper, and vitamin B12. 6 raw eastern oysters (85 grams or 3 ounces) give you 575% of the RDI for vitamin B12. [7] [8]
3.5 ounces (100 grams) of oysters provides 435 mg of omega-3s!
4.) Sardines
You either love sardines, or you don’t. These small, oily fish are usually eaten as a snack, delicacy, or appetizer. They’re a convenient, nutritious, fatty keto food for when you’re on the go. You might be surprised to hear sardines contain almost every nutrient your body needs.
You can obtain 96% of the RDI for selenium, 24% for vitamin D, and over 200% for vitamin B12 if you eat just 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of drained sardines! When it comes to omega-3s, you can find 1,480 mg in 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of sardines. [9]
5.) Cod Liver Oil
The livers of codfish are extracted to make cod liver oil. Many people take a cod liver oil supplement to increase omega-3 fatty acids. This oil is also brimming with nutrients like vitamins D and A. [10]
One tablespoon of cod liver oil has 2,682 mg of omega-3s.
6.) Herring
Herring is often pickled, cold-smoked, or sold as a pre-cooked, canned snack. This medium-sized fish is a popular breakfast food in some countries. In England, herring is served with eggs and called kippers.
Herring also contains vitamins B12 and D and almost 100% of the RDI for selenium. 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of herring has 2,366 mg of omega-3s. [11]
7.) Anchovies
Popular, tiny, and oily, anchovies are typically eaten in small portions, stuffed in olives, rolled around capers, or used as a topping for salad or pizza.
Anchovies are potent and used to flavor a range of dishes and sauces, including remoulade and Worcestershire sauce.
Boned anchovies are a good source of calcium. Selenium, niacin, and omega-3s can also be found in anchovies. 3.5 ounces (100 grams) of anchovies give you 2,113 mg of omega-3s! [12]







8.) Caviar
Most people consider caviar a luxurious delicacy only to be eaten on special occasions or used in smaller quantities as a garnish, taster, or starter. Caviar is essentially fish eggs (roe).
Caviar has a high content of choline and provides 1,086 mg of omega-3s per tablespoon (14.3 grams). [13]
9.) Flax Seeds
For vegetarians and vegans seeking omega-3s, flax seeds are one of the top food sources. These small yellow or brown seeds are usually milled, ground, or used to make oil.
Flax seeds are a rich plant-food source of the omega-3 fat alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Flaxseed oil can be used as a plant-based omega-3 supplement. Remember, the body converts ALA into the other omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA, and this process is inefficient in humans.
Flax seeds also provide magnesium and fiber. One tablespoon (10.3 grams) of whole flax seeds has 2,350 mg of omega-3s. [14]
Try a keto recipe featuring flax seeds:
- Keto porridge! (low-carb oatmeal)
- Crispy battered broccoli bites
- Keto Noatmeal overnight oats
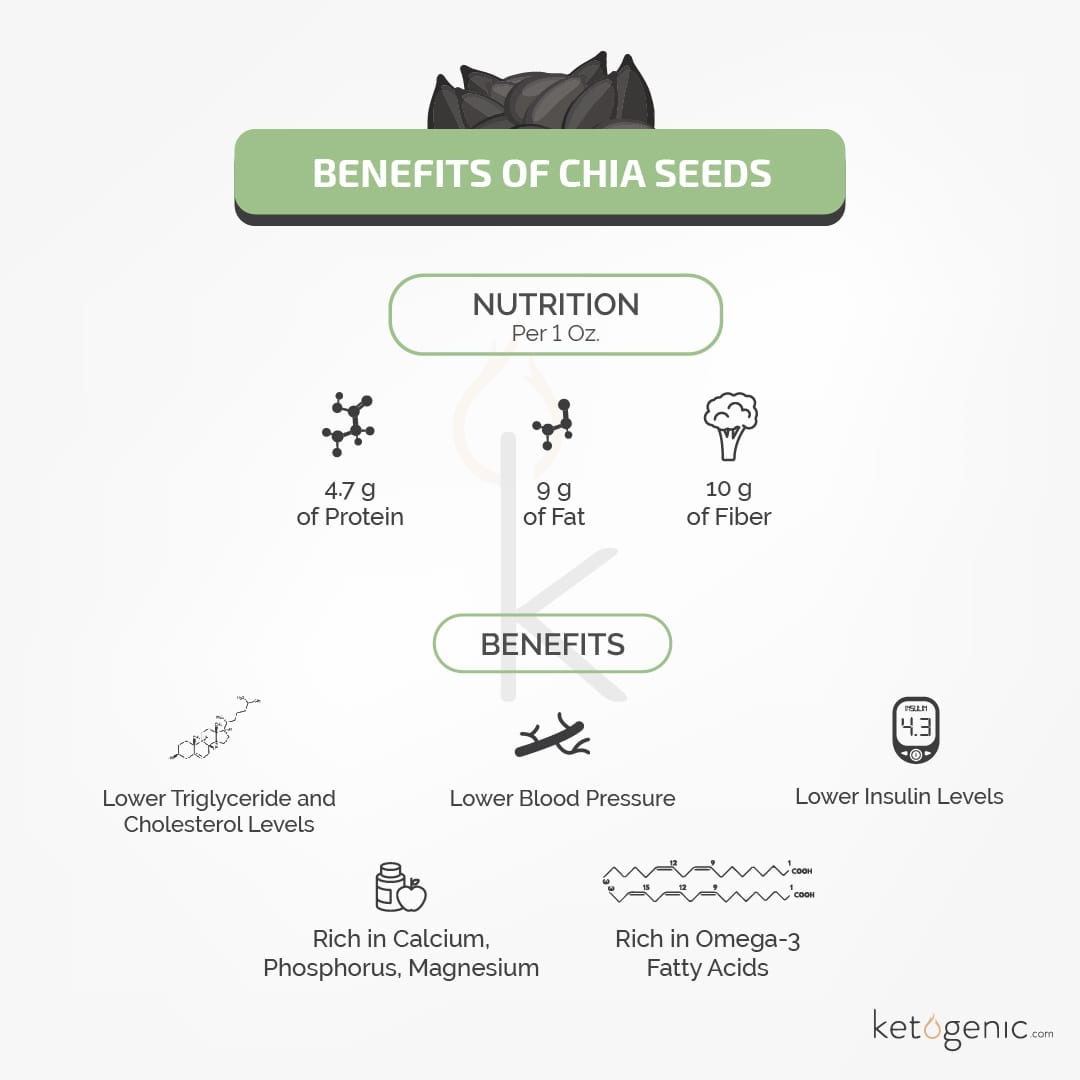
10.) Chia Seeds
Chia seeds are delicious and nutritious, and they can be used as an egg replacement in keto vegetarian and vegan recipes. Chia seeds are loaded with manganese, magnesium, selenium, and eight essential amino acids.
One ounce (28 grams) of chia seeds gives you 5,060 mg of omega-3s. [15]
Get creative with chia seeds in your kitchen and try a keto raspberry chia seed pudding, keto cereal, or keto trail mix!
11.) Soybeans
Soybeans are a popular vegetarian and vegan source of protein and fiber. Soybeans also contain other nutrients like folate, vitamin K, potassium, and magnesium.
Keep in mind soybeans are high in omega-6 fatty acids, and researchers have associated eating omega-6 in excess with inflammation. Inflammation is considered a key player in numerous chronic diseases. [16] [17]
3.5 ounces (100 grams) of soybeans delivers 1,443 mg of omega-3s!
Try this keto tofu pudding!
12.) Walnuts
Go nutty with walnuts and add them to salads, desserts, and more. Walnuts provide copper, manganese, beneficial plant compounds, and vitamin E. [18]
The skin of the walnut contains most of the phenol antioxidants, which offer the most health benefits. About 14 walnut halves (one ounce or 28 grams) have 2,570 mg of omega-3s!
Choose a walnutty recipe from Ketogenic.com!



Concluding Thoughts
Remember, animal foods, seafood, and algae have the omega-3 fats DHA and EPA, which are the most advantageous fatty acids. The omega-3 ALA is inferior to the other two and can be found in plant foods.
Other foods also have omega-3s in lesser amounts, such as eggs, meats, and dairy products from grass-fed animals, hemp seeds, and veggies like Brussel sprouts and spinach.
Consuming a balanced, ketogenic diet rich in whole foods can provide you with plenty of omega-3s.
Omega-3s give you health benefits like reducing inflammation and the risk of heart disease.
Peruse our recipe section for countless omega-3 rich keto recipes for breakfast, lunch, dinner, or snacks!
If you think you’re lacking in omega-3s and you don’t eat many of these foods, you might want to consider taking omega-3 supplements.
References
United States Department of Agriculture & United States Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010. DietaryGuidelines2010 (health.gov)
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Consultation on Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition. (2008). Interim Summary of Conclusions and Dietary Recommendations on Fats and Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition, Microsoft Word - FatsFA summary Rec Concl_17 May 2010-Final with LOP + DHA page7 corrections 31May 10.doc (who.int)
Su, K-P., Huang, S-Y., Chiu, C-C., & Shen, W. W. (2003). Omega-3 fatty acids in major depressive disorder. A preliminary double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 13(4), 267-71. DOI: 10.1016/s0924-977x(03)00032-4
Wang, C., Harris, W. S., Chung, M., Lichtenstein, A. H., Balk, E. M., Kupelnick, B., Jordan, H. S., & Lau, J. (2006). n-3 fatty acids from fish or fish-oil supplements, but not alpha-linolenic acid, benefit cardiovascular disease outcomes in primary- and secondary- prevention studies: A systematic review. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 84(1), 5-17. DOI: 10.1093/ajcn/84.1.5
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Salmon, Atlantic, Wild, Cooked, Dry Heat. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Mackerel, Salted. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Mollusks, Oyster, Eastern, Farmed, Raw. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Mollusks, Oyster, Pacific, Raw. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Sardine, Atlantic, Canned in Oil, Drained Solids with Bone. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish Oil, Cod Liver. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Herring, Atlantic, Kippered. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Anchovy, European, Canned in Oil, Drained Solids. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Fish, Caviar, Black and Red, Granular. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Seeds, Flaxseeds. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Seeds, Chia Seeds, Dried. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Soybeans, Mature Seeds, Dry Roasted. FoodData Central (usda.gov)
Patterson, E., Wall, R., Fitzgerald, G. F., Ross, R. P., & Stanton, C. (2012). Health implications of high dietary omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Nutr Metab, DOI: 10.1155/2012/539426
United States Department of Agriculture Food Database. Nuts, Walnuts, English. FoodData Central (usda.gov)









