Cauliflower is versatile, flavorful, satiating, nutritious, and keto-friendly. Let’s delve into the benefits of cauliflower and the many recipes you can try in your keto kitchen. Cauliflower is a cruciferous veggie, which means it’s particularly healthy for most people and has unique beneficial properties.
What are the Benefits of Cauliflower?
Cauliflower is a significant source of nutrients. It also contains unique plant compounds that might reduce your risk of several diseases, including cancer and heart disease. Cauliflower is weight-loss friendly and easy to incorporate into your ketogenic diet. Here are just some of the many benefits of cauliflower:
1. Packed with Nutrition!
Cauliflower has plenty of vitamins and few calories. It contains almost every mineral and vitamin you need, including:
2. Rich Fiber-Source
Cauliflower is high in fiber, which is beneficial for digestive and overall health. One cup of this tasty sulfur-rich veggie contains 3 grams of fiber, which is 10% of your daily needs. Fiber feeds healthy bacteria in your gut that help promotes digestive health and reduce inflammation [2] [3].
Consuming sufficient fiber might help prevent digestive conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), diverticulitis, and constipation. Studies show a diet high in fiber-rich veggies (like cauliflower) is associated with a lower risk of various illnesses, including diabetes, cancer, and heart disease. Fiber might also help with weight loss because it promotes fullness and might reduce overall calorie intake [4] [5] [6] [7].
3. Antioxidant-Rich
Antioxidants can protect your cells from inflammation and harmful free radicals. Like other cruciferous vegetables, cauliflower is high in isothiocyanates and glucosinolates – two antioxidant groups that have proven to slow the growth of cancer cells [8] [9] [10] [11].
Cauliflower also contains high amounts of vitamin C, which acts as an antioxidant and has anti-inflammatory effects in the body [12].
4. Rich in Sulforaphane
Cauliflower is rich in sulforaphane. This is an extensively studied antioxidant that’s been shown to help suppress cancer development by inhibiting enzymes involved in tumor and cancer growth [13] [14].
Sulforaphane seems to be most protective against prostate and colon cancer. Some research has also studied for its effects on other cancers, such as breast and pancreatic. Sulforaphane might also reduce high blood pressure and improve artery health, which could help prevent heart disease [15] [16].
5. Easy to Add to Your Diet
The famous cauliflower makes an incredibly versatile and filling low-carb replacement for carb-heavy comfort foods like rice and mash. Many keto dieters use cauliflower to replace legumes and grains in the diet.
Cauliflower is significantly lower in carbohydrates compared to grains and legumes. One cup of cauliflower contains 5 grams of carbs. Compare that to one cup of rice, which contains 45 grams of carbs [17].
Keto-Friendly Cauliflower Recipes
Cauliflower makes a great alternative for rice, pasta, mash, and beyond. You can steam, sauté, or roast cauliflower, and it’s usually fairly cheap and widely available. Here are just some of the many ways you can include cauliflower in your keto diet:
- Noatmeal Cauli Oats
- Salmon Over Spinach Risotto
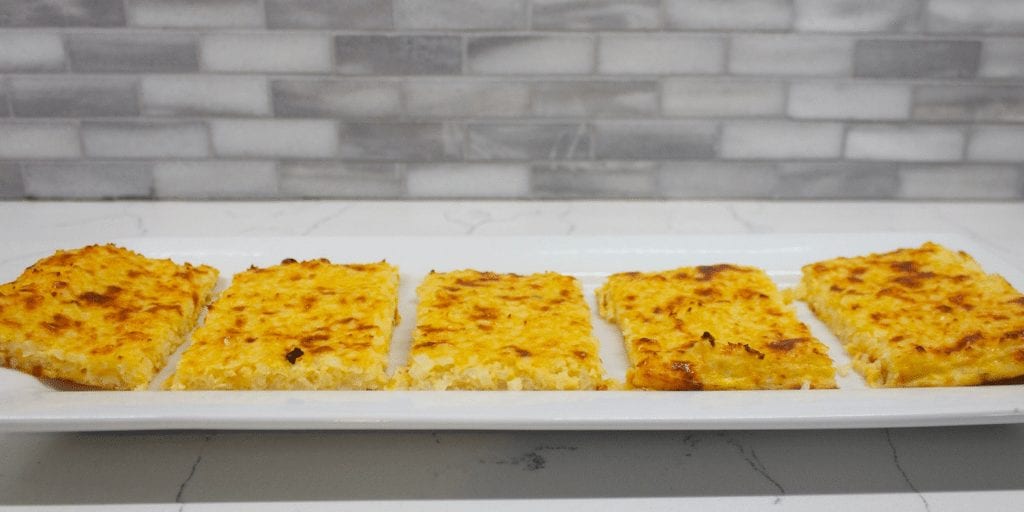
- Keto Corn Fritters
- Keto Cauli Bread
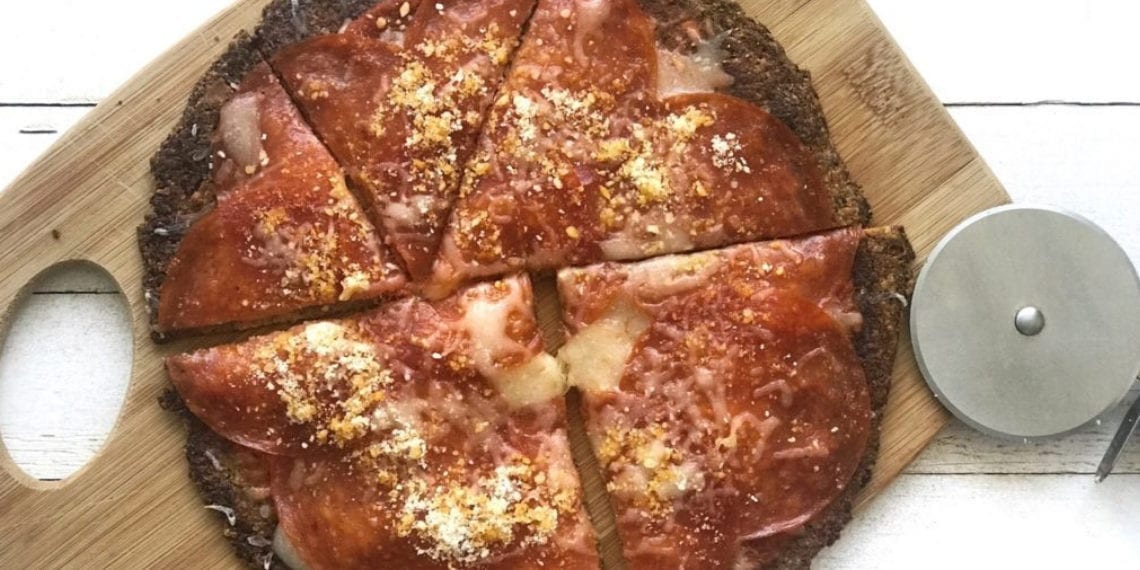
- Cauli Pizza
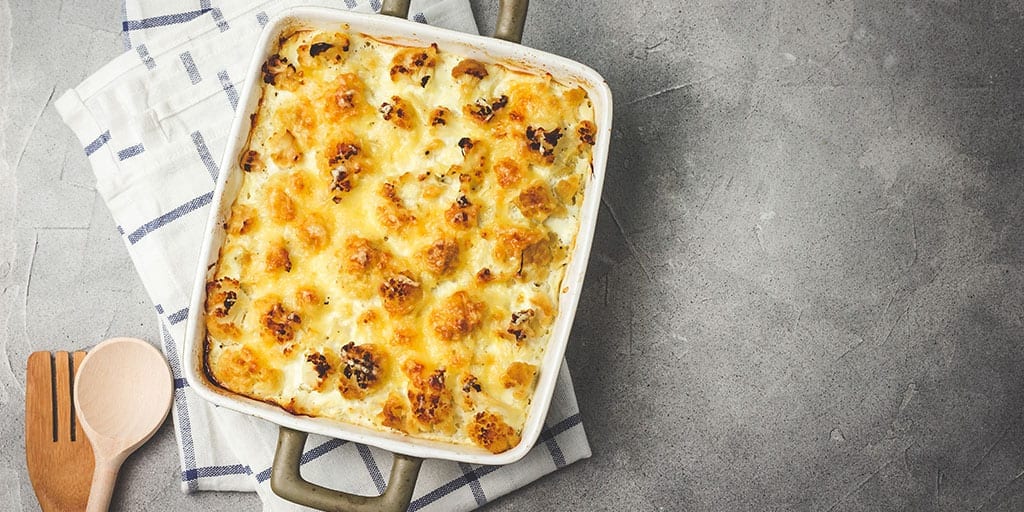
- Cauliflower Au Gratin
- Cauli Mac N Cheese
- Mashed Cauliflower
- Keto Buffalo Mac N Cheese
- Cauli Hashbrowns
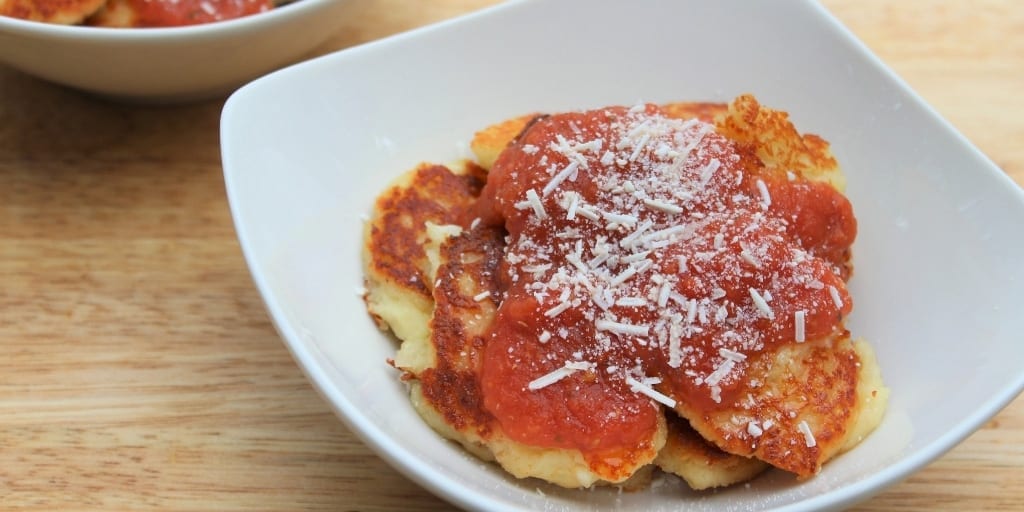
- Cauliflower Gnocchi
- Cauliflower Tabbouleh
Do You Eat Cauliflower on Your Ketogenic Diet?
Share your favorite cauliflower recipes and dishes with the keto community!
References
Self Nutrition Data. Cauliflower, Raw, Nutrition Facts & Calories.
Slavin, J. (2013). Fiber and prebiotics: Mechanisms and health benefits. Nutrients, 5(4), 1417-1435.
Otles, S., & Ozgoz, S. (2014). Health effects of dietary fiber. Acta Sci Pol Technol Aliment, 13(2), 191-202.
Slavin, J. L., & Lloyd, B. (2012). Health benefits of fruits and vegetables. Advances in Nutrition, 3(4), 506-516.
Bradbury, K. E., Appleby, P. N., & Key, T. J. (2014). Fruit, vegetable, and fiber intake in relation to cancer risk: Findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Anderson, J. W., Baird, P., Davis Jr, R. H., Ferreri, S., Knudston, M., Koraym, A., Waters, V., & Williams, C. L. (2009). Health benefits of dietary fiber. Nutrition Reviews, 67(4), 188-205.
Slavin, J. L. (2005). Dietary fiber and body weight. Nutrition, 21(3), 411-418.
Razis, A. F. A., & Noor, N. M. (2013). Cruciferous vegetables: Dietary phytochemicals for cancer prevention. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 14(3), 1565-1570.
Higdon, J. V., Delage, B., Williams, D. E., & Dashwood, R. H. (2007). Cruciferous vegetables and human cancer risk: Epidemiologic evidence and mechanistic basis. Pharmacol Res, 55(3), 224-236.
Keck, A-S., & Finley, J. W. (2004). Cruciferous vegetables: Cancer protective mechanisms of glucosinolate hydrolysis products and selenium. Integr Cancer Ther, 3(1), 5-12.
De Figueiredo, S. M., Filho, S. A. V., Nogueira-Machado, J. A., & Caligiorne, R. B. (2013). The anti-oxidant properties of isothiocyanates: A review. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, 7(3), 213-225.
Padayatty, S. J., Katz, A., Wang, Y., Eck, P., Kwon, O., Lee, J-H., Chen, S., Corpe, C., Dutta, A., Dutta, S. K., & Levine, M. (2003). Vitamin c as an antioxidant: Evaluation of its role in disease prevention. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 22(1), 18-35.
De Figueiredo, S. M., Binda, N. S., Nogueira-Machado, J. A., Vieira-Filho, S. A., & Caligiorne, R. B. (2015). The antioxidant properties of organosulfur compounds (sulforaphane). Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov, 9(1), 24-39.
Tortorella, S. M., Royce, S. G., Licciardi, P. V., & Karagiannis, T. C. (2015). Dietary sulforaphane in cancer chemoprevention: The role of epigenetic regulation and HDAC inhibition. Antioxidant Redox Signal, 22(16), 1382-1424.
Clarke, J. D., Dashwood, R. H., & Ho, E. (2008). Multi-targeted prevention of cancer by sulforaphane. Cancer Lett, 269(2), 291-304.
Bai, Y., Wang, X., Zhao, S., Ma, C., Cui, J., & Zheng, Y. (2015). Sulforaphane protects against cardiovascular disease via Nrf2 activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
Self Nutrition Data. Rice, White, Long Grain, Regular, Cooked, Nutrition Facts & Calories.