As the ketogenic diet is becoming a popular lifestyle globally, you must have heard about it too. Why is it becoming the talk of an hour? Does the keto diet really work? This query is solved with evidence ahead!
What is the Ketogenic Diet?
The ketogenic diet is a low-carb, moderate-protein, high-fat diet. On the keto diet,60- 70% of total daily calories from fats, 30-35% proteins, and 5-10% carbs.
By reducing carbohydrate intake and increasing fat intake, your body is forced into the metabolic state known as ketosis. Instead of running on glucose from carbohydrates for fuel, your liver will break down fatty acids and convert them into ketones.
To keep your body in ketosis, it is imperative to consume foods low in carbs.

Examples of low-carb foods that are packed full of healthy fats include nuts, seeds, olives, meat, fish, healthy oils (like avocado and olive oil), and eggs.
Not only is keto great for general weight loss, but research shows it is also effective in the management of obesity and other chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular disease. This low carb and high-fat diet results in tremendous weight loss along with mitigating the other health disorders.
But does the keto diet really work? Is it suitable for overall health? Unlike other diets, it isn’t only for weight loss, the keto diet improves the overall body mechanisms and human performance.
Weight Loss
A ketogenic diet plays an important role in losing weight. It provides you the perfect way to consume nutrient-dense foods without any empty calories.
The average ketogenic dieter consumes meals that include a protein source, green veggie, and healthy fats. An example of an average meal would be salmon and broccoli or chicken and Brussels sprouts.
The combinations of high-quality protein, nutrient-dense leafy green veggies, and healthy fats help keep you full and satisfied. Ketogenic meals decrease satiation and lead to fewer calories consumed. For more info on keto for weight loss, check out these articles:

Diabetes Prevention
Diabetes is a disorder of glucose metabolism. Type II diabetes is caused by impaired insulin receptor function. Since the body can not sense that insulin is binding to the receptor to trigger a sequence of events that allows glucose intake into cells, blood glucose levels remain elevated.
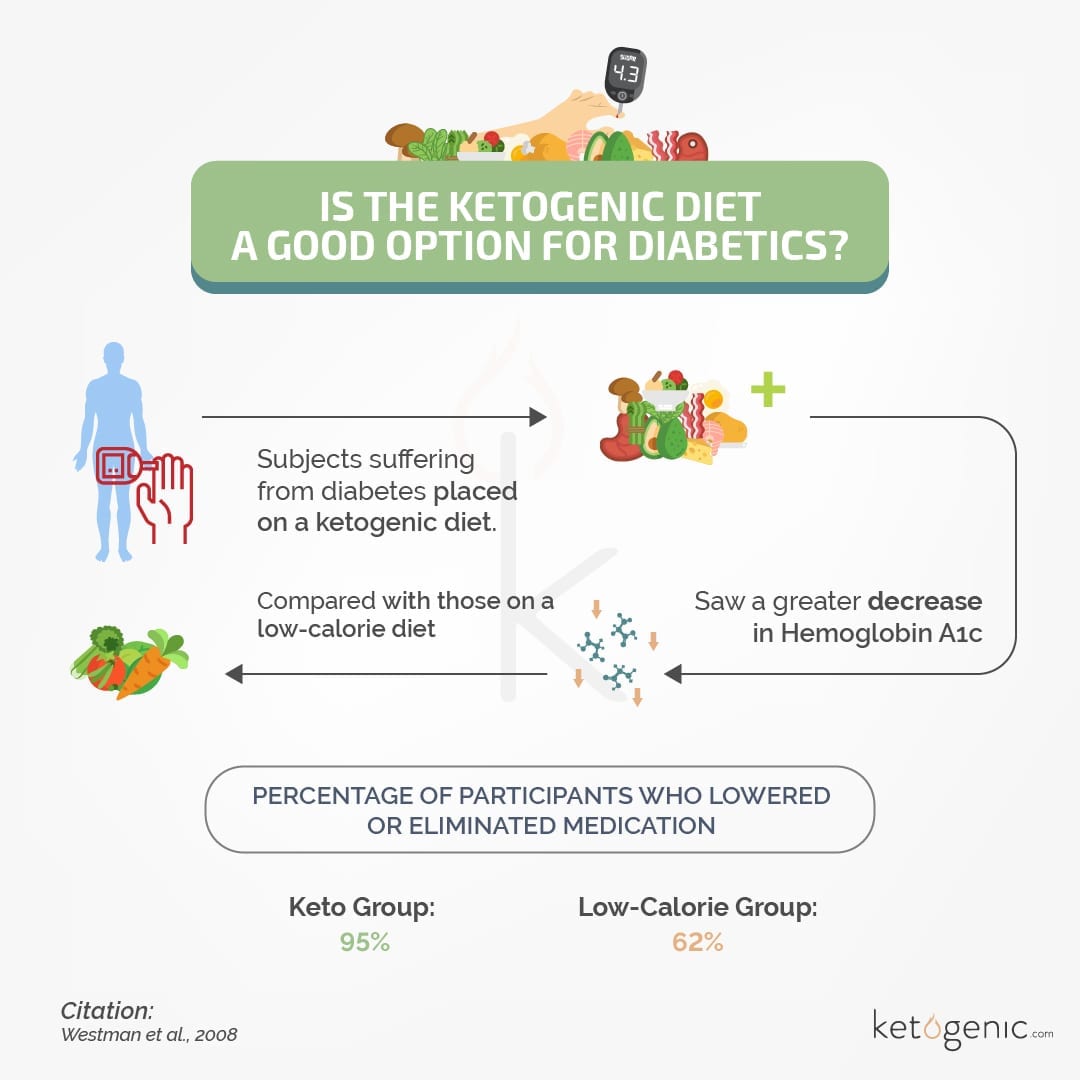
Since glucose is stuck floating in the blood instead of entering cells, cells can starve from the lack of a fuel source.
Since the ketogenic diet is a low-sugar diet, going keto helps reduce blood glucose levels. This reduction in glucose also helps resensitize insulin receptors, since they are no longer consistently bombarded by the presence of glucose.
For more information on keto for diabetes, check out these articles:
Cardiovascular disease
A ketogenic diet manages various risk factors such as cholesterol levels, maintains the lipid profile, and controls blood pressure. Keto may also reduce diastolic blood pressure and triglycerides levels.
For more information on keto for cardiovascular diseases, check out these articles:
Cancer
Cancer cells use glucose as fuel so that it may grow and spread. Reducing glucose intake may not only help prevent further tumor growth, but it may actually help reduce tumor size.
For more information on keto for cancer, check out these articles:
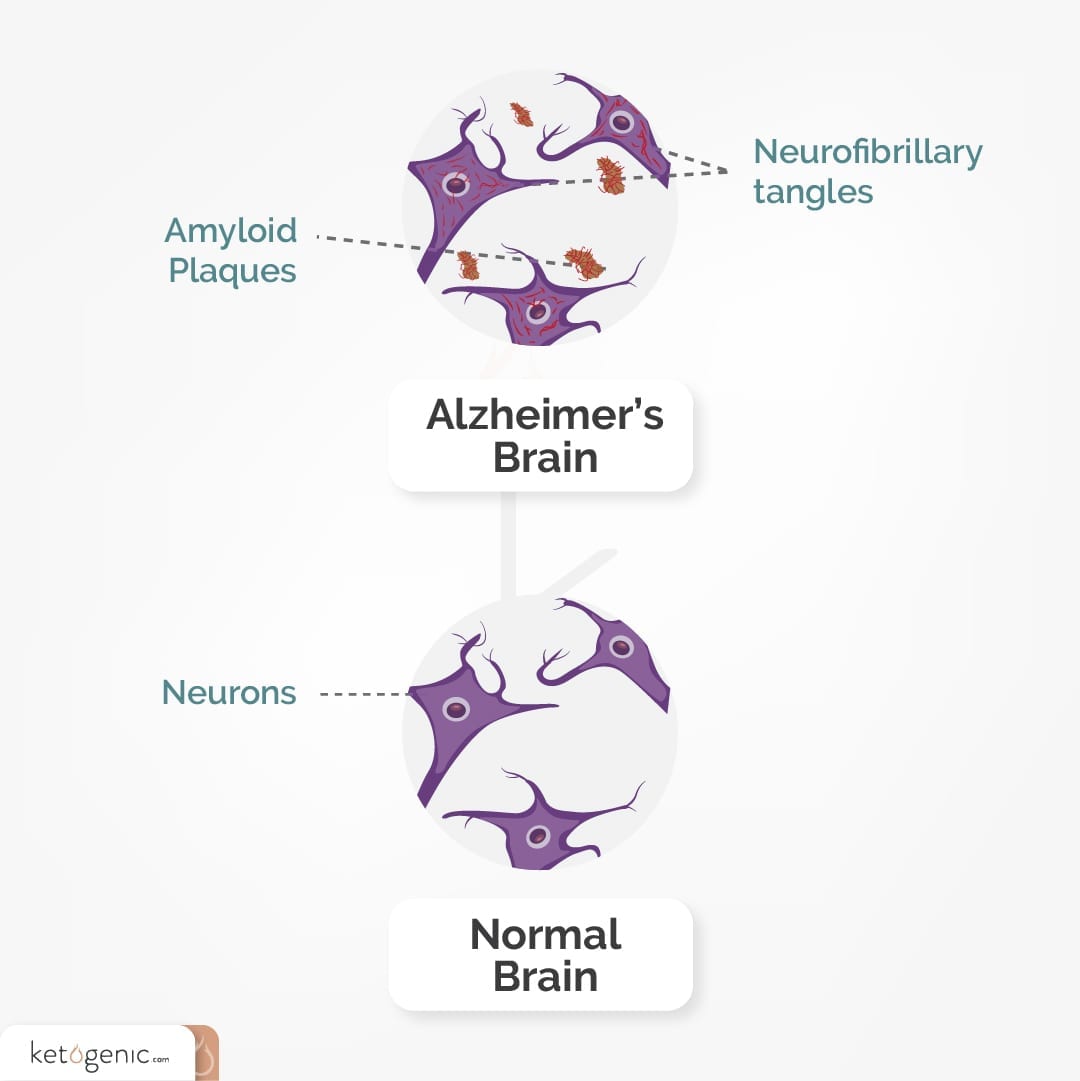
Alzheimer's Disease
The ketogenic diet has been shown to be beneficial for many neurodegenerative diseases. The key reason behind this is the fact ketones provide an alternative fuel source to the brain when glucose metabolism is otherwise impaired.
For more information on keto for Alzheimer’s Disease, check out these articles:
Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet was originally founded as a treatment for childhood, drug-resistant epilepsy. Research studies have shown that a ketogenic diet can cause a substantial decrease in seizures in children who are epileptic. A high-fat diet is well known to control epileptic attacks.
For more information on keto for epilepsy, check out these articles:
Parkinson's Disease
Similar to Alzheimer’s Disease, going keto may help Parkinson’s Disease symptoms by providing an alternative fuel source to the brain (aka ketones) when glucose metabolism is impaired.
For more information on keto for Parkinson’s Disease, check out these articles:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
A ketogenic diet decreases insulin levels and reduces inflammation, two key factors in PCOS. Plus, going keto can help normalize hormones and stabilize PCOS symptoms.
For more information on keto for PCOS, check out these articles:
Athletic Performance
Recently, low-carb diets have gained more popularity in the athletic community. But, does the keto diet really work to enhance athletic performance?
Research shows that once athletes are keto-adapted, yes, athletic performance can be enhanced.
One study shows that the long-term (>4wk) performances by keeping skilled athletes on a low-carbohydrate high-fat diet ketogenic diet (LCKD), performance improved. The results of the fat oxidation in the LCKD group were greater all over the 100 km time trial (TT). [1]
It was concluded that the low carbohydrate group, with 12 weeks of keto-adaptation, experienced increased fat oxidation during exercise and training, enhancement in the body composition, and improvement in overall performance relative to athletic activities. [1]
For more information on keto for athletic performance, check out these articles:
References
McSwiney. T. F, et al. (2017). Department of sports, exercise science, Waterford institute of technology, Waterford Ireland: Keto-adaptation enhances exercise performance and body composition responses in endurance athletes, 81(3), 25-34.